Universal Dependencies tools
This page collects links to and minimal instructions for tools related to Universal Dependencies.
If you would like to have your tool added to this page, please write the UD mailing list.
Listing
- Tools maintained by the UD project
- Annotation statistics
- Consistency checking
- Data validation
- Format conversion
- Third-party tools
- Annotation tools
- Editor modes
- Processing tools
- Visualization tools
UD-maintained tools
The Universal Dependencies project maintains a number of core tools for working with UD data. These tools are available from https://github.com/universaldependencies/tools and briefly described below.
Annotation statistics
There are two scripts that compute statistics, one written in Python and one in Perl. Despite similar names they are not equivalent!
python conllu-stats.py -h python conllu-stats.py --stats ../UD_English/en-ud-train.conllu perl conllu-stats.pl --help
The Perl script can be run in two main modes. In the default mode, it generates a XML file with statistics, including all tags, features and relations. This file is generated by the release team for every released treebank and the file stats.xml is then part of the release. The script is typically invoked from the treebank folder:
cat *.conllu | perl conllu-stats.pl > stats.xml
In the other mode, the script generates much more detailed statistics, which are then automatically included at appropriate places of the language-specific documentation. In this case the script needs to know where are all the treebank repositories and where is the docs repository. It will process all treebanks of one language in one run because there is only one docs section per language. It will write the statistics to the docs repository, which must be switched to the pages-source branch and must be afterwards pushed back to Github. This is usually also done at release time for all languages.
perl conllu-stats.pl --detailed --data .. --docs ../docs --lang pt
Consistency checking
(Description TODO)
Data validation
Validation of UD released treebanks is done using the script validate.py from the tools repository. More details are given
on the release checklist page.
Format conversion
See Issue 376 for references to software that helps with migration of treebanks from UD v1 to v2 guidelines.
Third-party tools
Annotation Tools
brat rapid annotation tool
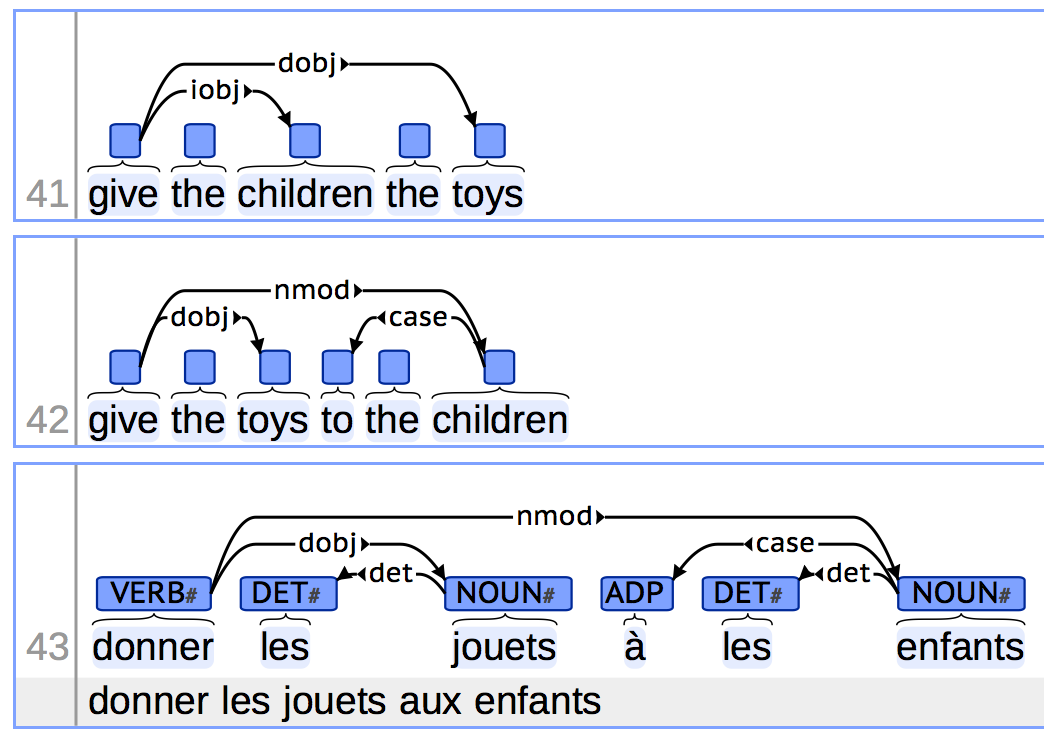 brat is a browser-based tool for text annotation. The brat visualization component is used in the UD documentation system and the tool comes with a custom configuration allowing it to be used for UD annotation .
brat is a browser-based tool for text annotation. The brat visualization component is used in the UD documentation system and the tool comes with a custom configuration allowing it to be used for UD annotation .
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: any (browser-based)
- Implementation: Python (server), JavaScript (client)
- License: MIT (open source)
- Homepage: http://brat.nlplab.org/
- References: Stenetorp et al. (2012)
WebAnno
WebAnno is a general purpose web-based annotation tool for a wide range of linguistic annotations including various layers of morphological, syntactical, and semantic annotations. Additionaly, custom annotation layers can be defined, allowing WebAnno to be used also for non-linguistic annotation tasks. WebAnno targets annotation teams in which all annotators work independently from each other. The tool includes facilities for curating/merging the annotations from multiple annotators, calculating inter-annotator agreement, and project management. Additional features include a correction and automation mode as well as decent support for right-to-left languages.
Since version 3.0.0, WebAnno supports importing and exporting data in the CoNLL-U format. If the data contains sub-token annotations, then the text is obtained from the subtokens and the surface text is added as annotations. To control which column dependencies end up in, the flavor feature of the built-in dependency layer needs to be used. If the feature is set to enchanced, then it goes to the enhanced dependencies column, otherwise to the basic dependencies column. It is currently up to the annotator to ensure that the dependency trees are well-formed and representable in CoNLL-U, otherwise export to CoNLL-U may fail.
WebAnno 3.0.0 does not support the CoNLL-U 2.0 format at this time.
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: client: any (browser-based), server: Java
- Implementation: Java (server), JavaScript (client)
- License: Apache License 2.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://webanno.github.io/webanno/
- References: see WebAnno website
DgAnnotator
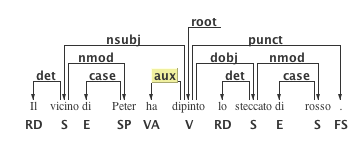 DgAnnotator (Dependency Graph Annotator) is a visual tool for annotating text with syntactic information, in particular creating a dependency tree. The tool reads and produces annotated documents in both XML, CoNLL-X and CoNLL-U tab separated format. Additional features: shows the differences, highlighted in red, between two different dependency trees on the same corpus; generates PNG snapshots of trees; performs PoS tagging and parsing connecting to a network service; panning and zooming.
DgAnnotator (Dependency Graph Annotator) is a visual tool for annotating text with syntactic information, in particular creating a dependency tree. The tool reads and produces annotated documents in both XML, CoNLL-X and CoNLL-U tab separated format. Additional features: shows the differences, highlighted in red, between two different dependency trees on the same corpus; generates PNG snapshots of trees; performs PoS tagging and parsing connecting to a network service; panning and zooming.
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Windows, Linux, OS X
- Implementation: Java
- License: GPL (open source)
- Homepage: http://medialab.di.unipi.it/Project/QA/Parser/DgAnnotator/
- References: Giuseppe Attardi
UD Annotatrix
UD Annotatrix is a browser-based offline + online annotation tool for dependency trees aimed at the UD community. It supports a number of features, including validation and two-level tokenisation.
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Any
- Implementation: Python, JavaScript
- License: GPL-3.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://github.com/jonorthwash/ud-annotatrix
- References: Tyers, F. M., Sheyanova, M. and Washington, J. N. (2018) “UD Annotatrix: An annotation tool for Universal Dependencies”. Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Treebanks and Linguistic Theories
Tred
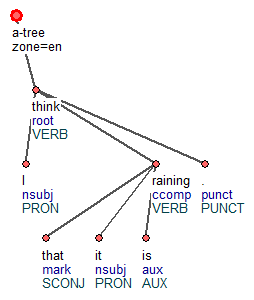 Tred (Tree Editor) is a graph visualization and manipulation program written in Perl. It was the main tool used to annotate the Prague treebanks. It supports macros (in Perl) to automate frequently repeated operations. There are extensions for various annotation layers such as MWEs or coreference. Since January 2018, there is also an extension for CoNLL-U files (including multi-word tokens and enhanced dependencies).
Tred (Tree Editor) is a graph visualization and manipulation program written in Perl. It was the main tool used to annotate the Prague treebanks. It supports macros (in Perl) to automate frequently repeated operations. There are extensions for various annotation layers such as MWEs or coreference. Since January 2018, there is also an extension for CoNLL-U files (including multi-word tokens and enhanced dependencies).
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Windows, Linux, OS X
- Implementation: Perl
- License: GPL (open source)
- Homepage: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/tred/
- References: Petr Pajas, Peter Fabian, Jan Štěpánek
Arborator
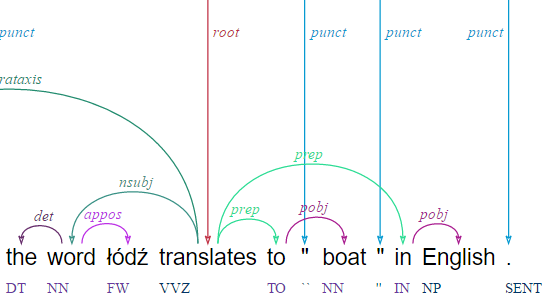
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Any
- Implementation: Python, JavaScript
- License: AGPL-3.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://arborator.ilpga.fr/
- References: Gerdes, Kim (2013), Collaborative Dependency Annotation. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Dependency Linguistics (DepLing 2013). Prague, 88–97.
LightTag
LightTag is a general purpose text annotation tool which supports span annotations, classification as well as phrase-based and dependency-based relations. LightTag allows a drag-and-drop interface allowing annotators to easily drag individual tokens or sub-trees to construct their parse.
LightTag’s Universal Dependency Tool allows the user to paste an existing CoNLL-U file, visualize and correct the annotations. LightTag’s full featured text annotation tool supports managing teams of annotators, is fully hosted and availble free for academic use.
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Web
- Implementation: Python, JavaScript
- License: See terms of use
- Homepage: https://lighttag.io/
- Contact: udep@lighttag.io
TrUDucer
TrUDucer is a tree rewriting system based on tree transducers. It transforms dependency trees in a top-down fashion, making sure that each resulting structure will still be a valid tree. Rules are written in a domain-specific language; for cases where the DSL is not powerfui enough, rules can be augmented by writing special-case predicates in groovy. It contains an interactive transformation viewer to debug rule applications and a search tool to find trees where a specific rule could be applicable. As of 2018, TrUDucer is under active development at Hamburg University.
An example rule file converting (large parts of) the Hamburg Dependency Treebank to UD is provided with TrUDucer. The Univerity of Zurich provides a rule file to convert the TIGER treebank to UD using TrUDucer.
- Category: automatic conversion tool
- Platform: Any
- Implementation: Java
- License: GPLv3 (open source)
- Homepage: http://nats.gitlab.io/truducer/
- References: Hennig, Felix and Köhn, Arne (2017), Dependency Tree Transformation with Tree Transducers. In: Proceedings of the NoDaLiDa 2017 Workshop on Universal Dependencies (UDW 2017). Gothenburg, 58–66.
- Contact: arne@chark.eu
ConlluEditor
ConlluEditor is a tool which facilitates the editing of syntactic relations and morphological features of files in CoNLL-U format. It uses a Java-based server and a HTML/CSS/Javascript based front-end. The editor loads the CoNLL-U file and saves every change to disk (and performs a git commit if the file is under git version control).
The editor provides the following functionalities:
- editing words (forms, lemmas, upos, xpos, features, enhanced dependencies
- editing dependency relations
- join/split words (to correct tokenization errors)
- join/split sentences (to correct tokenization errors)
- undo/redo (partially)
-
git support
- Category: manual annotation tool
- Platform: Any
- Implementation: Java, JavaScript
- License: BSD-3-Clause (open source)
- Homepage: https://github.com/Orange-OpenSource/conllueditor
- Contact: johannes.heinecke@orange.com
Editor modes
Emacs
conllu-mode is an Emacs mode for editing CoNLL-U files (syntax highlighting, column alignment, shortcuts for navigation, etc).
- Category: editor
- Platform: any OS that runs Emacs
- Implementation: Emacs Lisp
- License: GPL 3.0
- Homepage https://github.com/odanoburu/conllu-mode
Atom
This package provides syntax highlighting for CoNLL-U files in Atom.
- Category: editor
- Platform: any OS that runs Atom
- Implementation: –
- License: Apache 2.0
- Homepage https://atom.io/packages/language-conllu
Sublime Text
Syntax highlighting for CoNLL-U files on Sublime Text.
- Category: editor
- Platform: any OS that runs Sublime Text
- Implementation: –
- License: Apache 2.0
- Homepage https://github.com/stephsamson/CoNLL-U.tmLanguage/
Processing tools
CL-CoNLLU
A Common Lisp library for various CoNLL-U-related operations. We have already functions for reading, writing, making queries, construct visualizations of sentences, compare trees etc.
- Category: library
- Platform: any OS that runs a Common Lisp implementation
- Implementation: Common Lisp
- License: Apache License
- Homepage: https://github.com/own-pt/cl-conllu/
- References: http://arademaker.github.io/bibliography/tilic-stil-2017.html
DepEdit
DepEdit is a simple, open source, configurable tool for manipulating dependency trees, written in Python (2/3). It can be run standalone from the commandline or imported as a module, and it is available on PyPI (pip install depedit). Main features:
- Identify target subtrees based on regex matching of token attributes, distance between tokens, and subgraph edges
- Change token attributes (incl. text, pos, morph, etc.)
- Use regex capturing groups in find/replace values (e.g. allows for collapsing captured prepositions into the deprel of the governing token)
- Connect different tokens in the tree by setting their head feature to one of the match objects
- Use external configuration files for different scenarios or define rules programmatically when used as a module
- No language or schema specific details are hardwired into the system - everything is defined in the configuration file
-
Can be used as a very rudimentary rule-based parser to pre-process data with easy dependencies before manual annotation (e.g. attach all articles to following nouns as
det) - Category: library
- Platform: Windows, Linux, OSX
- Implementation: Python 2/3
- License: Apache License 2.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://corpling.uis.georgetown.edu/depedit/
- References: see website
DKPro Core CoNLL-U reader/writer
DKPro Core is collection of software components for natural language processing (NLP) based on the Apache UIMA framework. DKPro Core can be used to build workflows that automatically process text using a wide range of NLP tools from third parties that are all interoperable (Stanford CoreNLP, Apache OpenNLP, ClearNLP, mate-tools, etc etc.). It also supports a range of different data formats and can be used to convert between the different supported formats.
Starting with version 1.9.0, DKPro Core supports reading and writing the CoNLL-U format.
The latest CoNLL-U 2.0 format is not yet supported.
- Category: UIMA component
- Platform: Windows, Linux, OS X
- Implementation: Java
- License: Apache License 2.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://dkpro.github.io/dkpro-core/
- References: see DKPro Core website
pyconll
pyconll is a minimal, entirely python, library for parsing and writing CoNLL-U files. pyconll allows users to easily parse out info from CoNLL-U corpora, or to perform and write corpus transformations. pyconll aims to provide a low-level interface over the CoNLL-U annotation scheme that is easy to understand and works with the current standard. Further, since it is written in python, there is no need to learn a new DSL or tool.
- Category: library
- Platform: Any OS with Python 3 implementation
- Implementation: Python 3
- License: MIT License
- Homepage: https://pyconll.github.io/
- Documentation: https://pyconll.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Treex
Treex is a modular natural language processing framework. It reads and writes data in many formats (including CoNLL-U) and provides API for dependency tree manipulation. Many treebanks have been harmonized in HamleDT and then converted to UD using Treex.
- Category: treebank processing framework
- Platform: tested mainly on Linux
- Implementation: Perl
- License: Perl
- Homepage: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/treex
- References: Popel and Žabokrtský (2010)
UDPipe
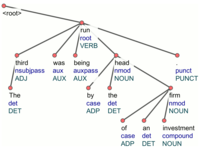 UDPipe is a trainable pipeline for tokenization, tagging, lemmatization and parsing of CoNLL-U files. UDPipe is language-agnostic and can be trained given only annotated data in CoNLL-U format. (Nevertheless, to train the tokenizer, either the
UDPipe is a trainable pipeline for tokenization, tagging, lemmatization and parsing of CoNLL-U files. UDPipe is language-agnostic and can be trained given only annotated data in CoNLL-U format. (Nevertheless, to train the tokenizer, either the SpaceAfter feature must be present, or at least some plain text must be available; also morphological analyzer and lemmatizer can be improved if morphological dictionary is provided.) Trained models are provided for nearly all UD treebanks. UDPipe is available as a binary, as a library for C++, Python, Perl, Java, C#, and as a web service.
- Category: trainable tokenizer, tagger, lemmatizer and parser
- Platform: Linux, Windows, OS X
- Implementation: C++; language bindings for Python, Perl, Java and C#
- License: MPL 2.0 (open source)
- Homepage: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/udpipe
- On-line service: http://lindat.mff.cuni.cz/services/udpipe/
- References: Milan Straka, Jan Hajič and Jana Straková 2016. UDPipe: Trainable Pipeline for Processing CoNLL-U Files Performing Tokenization, Morphological Analysis, POS Tagging and Parsing. LREC 2016, Portorož, Slovenia, May 2016.
UDAPI
- Category: libraries for various UD and CoNLL-U-related operations in several programming languages
- Implementation: Java, Perl, Python
- License: GPL, Perl
- Homepage: http://udapi.github.io/
Visualization tools
Deptreeviz
Deptreeviz is a SVG visualization and editing component. It can be used as a swing component or to create SVGs from the command line. It supports drag-and-drop modifications of trees, including dependency label and selecting the correct lexical items. For the editing facilities, a matching backend needs to be programmed. Deptreeviz is used to convert the Hamburg Dependency Treebank to UD.
- Category: tree visualization (SVG graphics)
- Platform: Any
- Implementation: Java
- License: Apache License 2.0 (open source)
- Homepage: https://gitlab.com/nats/deptreeviz
- References: Sven Zimmer, Arne Köhn
CoNLL-U viewer
A simple browser-based (JavaScript, i.e. client side) viewer of your CoNLL-U files. Open your file, see the tree, go to the next tree. Click on a node to see all its attributes. Save the tree as an SVG graphics if needed. There is no way of jumping directly to a tree, neither by tree number, nor by searching attribute values.
- Category: tree viewer
- Platform: any (browser-based)
- Implementation: JavaScript
- Credit: Milan Straka, Michal Sedlák
- Access here
CoNLL-U viewer at rug.nl
- Live site: http://www.let.rug.nl/kleiweg/conllu/
- Source code: Github
TüNDRA
TüNDRA (Tübingen aNnotated Data Retrieval Application) is a web application for searching in treebanks using a lightweight query language inspired by the widely used TIGERSearch application. It offers corpus linguists an interface for using corpora with complex annotation and syntactic links. Most of the treebanks available in TüNDRA are free and publicly available. To access all the treebanks a user has to have an account at a European institution of higher education (i.e. be a student or an employee). Any user may upload a CoNLL-U or a TCF file to browse/search it with the tool. A visualization is interactive (scaling, zooming, panning) and can be saved in multiple formats (e.g. to be later used for a publication). TüNDRA is a part of CLARIN-D project and is funded by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF).
- Category: tree viewer and search engine
- Platform: any (web application)
- Implementation: JavaScript, React (frontend), Java (backend)
- Credit: Department of General and Computational Linguistics at the University of Tübingen
- Access here