Ambiguity
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
(Learn how and when to remove this template message)
|

Ambiguity is a type of meaning in which a phrase, statement or resolution is not explicitly defined, making several interpretations plausible. A common aspect of ambiguity is uncertainty. It is thus an attribute of any idea or statement whose intended meaning cannot be definitively resolved according to a rule or process with a finite number of steps. (The ambi- part of the term reflects an idea of "two", as in "two meanings".)
The concept of ambiguity is generally contrasted with vagueness. In ambiguity, specific and distinct interpretations are permitted (although some may not be immediately obvious), whereas with information that is vague, it is difficult to form any interpretation at the desired level of specificity.
Context may play a role in resolving ambiguity. For example, the same piece of information may be ambiguous in one context and unambiguous in another.
Contents
Linguistic forms[edit]
Lexical ambiguity is contrasted with semantic ambiguity. The former represents a choice between a finite number of known and meaningful context-dependent interpretations. The latter represents a choice between any number of possible interpretations, none of which may have a standard agreed-upon meaning. This form of ambiguity is closely related to vagueness.
Linguistic ambiguity can be a problem in law, because the interpretation of written documents and oral agreements is often of paramount importance.
Lexical Ambiguity[edit]
The lexical ambiguity of a word or phrase pertains to its having more than one meaning in the language to which the word belongs. "Meaning" here refers to whatever should be captured by a good dictionary. For instance, the word "bank" has several distinct lexical definitions, including "financial institution" and "edge of a river". Or consider "apothecary". One could say "I bought herbs from the apothecary". This could mean one actually spoke to the apothecary (pharmacist) or went to the apothecary (pharmacy).
The context in which an ambiguous word is used often makes it evident which of the meanings is intended. If, for instance, someone says "I buried $100 in the bank", most people would not think someone used a shovel to dig in the mud. However, some linguistic contexts do not provide sufficient information to disambiguate a used word.
Lexical ambiguity can be addressed by algorithmic methods that automatically associate the appropriate meaning with a word in context, a task referred to as word sense disambiguation.
The use of multi-defined words requires the author or speaker to clarify their context, and sometimes elaborate on their specific intended meaning (in which case, a less ambiguous term should have been used). The goal of clear concise communication is that the receiver(s) have no misunderstanding about what was meant to be conveyed. An exception to this could include a politician whose "weasel words" and obfuscation are necessary to gain support from multiple constituents with mutually exclusive conflicting desires from their candidate of choice. Ambiguity is a powerful tool of political science.
More problematic are words whose senses express closely related concepts. "Good", for example, can mean "useful" or "functional" (That's a good hammer), "exemplary" (She's a good student), "pleasing" (This is good soup), "moral" (a good person versus the lesson to be learned from a story), "righteous", etc. " I have a good daughter" is not clear about which sense is intended. The various ways to apply prefixes and suffixes can also create ambiguity ("unlockable" can mean "capable of being unlocked" or "impossible to lock").
Syntactic Ambiguity[edit]
Semantic ambiguity happens when a sentence contains an ambiguous word or phrase—a word or phrase that has more than one meaning. In "We saw her duck" (example due to Richard Nordquist), the word "duck" can refer either
- to the person's bird (the noun "duck", modified by the possessive pronoun "her"), or
- to a motion she made (the verb "duck", the subject of which is the objective pronoun "her", object of the verb "saw").[2]
Syntactic ambiguity arises when a sentence can have two (or more) different meanings because of the structure of the sentence—its syntax. This is often due to a modifying expression, such as a prepositional phrase, the application of which is unclear. "He ate the cookies on the couch", for example, could mean that he ate those cookies that were on the couch (as opposed to those that were on the table), or it could mean that he was sitting on the couch when he ate the cookies. "To get in, you will need an entrance fee of $10 or your voucher and your drivers' license." This could mean that you need EITHER ten dollars OR BOTH your voucher and your license. Or it could mean that you need your license AND you need EITHER ten dollars OR a voucher. Only rewriting the sentence, or placing appropriate punctuation can resolve a syntactic ambiguity.[2] For the notion of, and theoretic results about, syntactic ambiguity in artificial, formal languages (such as computer programming languages), see Ambiguous grammar.
Spoken language can contain many more types of ambiguities which are called phonological ambiguities, where there is more than one way to compose a set of sounds into words. For example, "ice cream" and "I scream". Such ambiguity is generally resolved according to the context. A mishearing of such, based on incorrectly resolved ambiguity, is called a mondegreen.
Metonymy involves the use of the name of a subcomponent part as an abbreviation, or jargon, for the name of the whole object (for example "wheels" to refer to a car, or "flowers" to refer to beautiful offspring, an entire plant, or a collection of blooming plants). In modern vocabulary, critical semiotics,[9] metonymy encompasses any potentially ambiguous word substitution that is based on contextual contiguity (located close together), or a function or process that an object performs, such as "sweet ride" to refer to a nice car. Metonym miscommunication is considered a primary mechanism of linguistic humor.
Philosophy[edit]
Philosophers (and other users of logic) spend a lot of time and effort searching for and removing (or intentionally adding) ambiguity in arguments because it can lead to incorrect conclusions and can be used to deliberately conceal bad arguments. For example, a politician might say, "I oppose taxes which hinder economic growth", an example of a glittering generality. Some will think he opposes taxes in general because they hinder economic growth. Others may think he opposes only those taxes that he believes will hinder economic growth. In writing, the sentence can be rewritten to reduce possible misinterpretation, either by adding a comma after "taxes" (to convey the first sense) or by changing "which" to "that" (to convey the second sense) or by rewriting it in other ways. The devious politician hopes that each constituent will interpret the statement in the most desirable way, and think the politician supports everyone's opinion. However, the opposite can also be true – an opponent can turn a positive statement into a bad one if the speaker uses ambiguity (intentionally or not). The logical fallacies of amphiboly and equivocation rely heavily on the use of ambiguous words and phrases.
In continental philosophy (particularly phenomenology and existentialism), there is much greater tolerance of ambiguity, as it is generally seen as an integral part of the human condition. Martin Heidegger argued that the relation between the subject and object is ambiguous, as is the relation of mind and body, and part and whole.[3] In Heidegger's phenomenology, Dasein is always in a meaningful world, but there is always an underlying background for every instance of signification. Thus, although some things may be certain, they have little to do with Dasein's sense of care and existential anxiety, e.g., in the face of death. In calling his work Being and Nothingness an "essay in phenomenological ontology" Jean-Paul Sartre follows Heidegger in defining the human essence as ambiguous, or relating fundamentally to such ambiguity. Simone de Beauvoir tries to base an ethics on Heidegger's and Sartre's writings (The Ethics of Ambiguity), where she highlights the need to grapple with ambiguity: "as long as philosophers and they [men] have thought, most of them have tried to mask it...And the ethics which they have proposed to their disciples have always pursued the same goal. It has been a matter of eliminating the ambiguity by making oneself pure inwardness or pure externality, by escaping from the sensible world or being engulfed by it, by yielding to eternity or enclosing oneself in the pure moment." Ethics cannot be based on the authoritative certainty given by mathematics and logic, or prescribed directly from the empirical findings of science. She states: "Since we do not succeed in fleeing it, let us, therefore, try to look the truth in the face. Let us try to assume our fundamental ambiguity. It is in the knowledge of the genuine conditions of our life that we must draw our strength to live and our reason for acting". Other continental philosophers suggest that concepts such as life, nature, and sex are ambiguous. Corey Anton has argued that we cannot be certain what is separate from or unified with something else: language, he asserts, divides what is not, in fact, separate. Following Ernest Becker, he argues that the desire to 'authoritatively disambiguate' the world and existence has led to numerous ideologies and historical events such as genocide. On this basis, he argues that ethics must focus on 'dialectically integrating opposites' and balancing tension, rather than seeking a priori validation or certainty. Like the existentialists and phenomenologists, he sees the ambiguity of life as the basis of creativity.
Literature and Rhetoric[edit]
In literature and rhetoric, ambiguity can be a useful tool. Groucho Marx's classic joke depends on a grammatical ambiguity for its humor, for example: "Last night I shot an elephant in my pajamas. How he got in my pajamas, I'll never know". Songs and poetry often rely on ambiguous words for artistic effect, as in the song title "Don't It Make My Brown Eyes Blue" (where "blue" can refer to the color, or to sadness).
In the narrative, ambiguity can be introduced in several ways: motive, plot, character. F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the latter type of ambiguity with notable effect in his novel The Great Gatsby.
Mathematical notation[edit]
Mathematical notation, widely used in physics and other sciences, avoids many ambiguities compared to expression in natural language. However, for various reasons, several lexical, syntactic and semantic ambiguities remain.
Names of functions[edit]
The ambiguity in the style of writing a function should not be confused with a multivalued function, which can (and should) be defined in a deterministic and unambiguous way. Several special functions still do not have established notations. Usually, the conversion to another notation requires to scale the argument or the resulting value; sometimes, the same name of the function is used, causing confusions. Examples of such underestablished functions:
- Sinc function
- Elliptic integral of the third kind; translating elliptic integral form MAPLE to Mathematica, one should replace the second argument to its square, see Talk:Elliptic integral#List of notations; dealing with complex values, this may cause problems.
- Exponential integral[3]
- Hermite polynomial[3]:775
Expressions[edit]
Ambiguous expressions often appear in physical and mathematical texts. It is common practice to omit multiplication signs in mathematical expressions. Also, it is common to give the same name to a variable and a function, for example, . Then, if one sees , there is no way to distinguish whether it means multiplied by , or function evaluated at argument equal to . In each case of use of such notations, the reader is supposed to be able to perform the deduction and reveal the true meaning.
Creators of algorithmic languages try to avoid ambiguities. Many algorithmic languages (C++ and Fortran) require the character * as symbol of multiplication. The Wolfram Language used in Mathematica allows the user to omit the multiplication symbol, but requires square brackets to indicate the argument of a function; square brackets are not allowed for grouping of expressions. Fortran, in addition, does not allow use of the same name (identifier) for different objects, for example, function and variable; in particular, the expression f=f(x) is qualified as an error.
The order of operations may depend on the context. In most programming languages, the operations of division and multiplication have equal priority and are executed from left to right. Until the last century, many editorials assumed that multiplication is performed first, for example, is interpreted as ; in this case, the insertion of parentheses is required when translating the formulas to an algorithmic language. In addition, it is common to write an argument of a function without parenthesis, which also may lead to ambiguity. Sometimes, one uses italics letters to denote elementary functions. In the scientific journal style, the expression means product of variables , , and , although in a slideshow, it may mean .
A comma in subscripts and superscripts sometimes is omitted; it is also ambiguous notation. If it is written , the reader should guess from the context, does it mean a single-index object, evaluated while the subscript is equal to product of variables , and , or it is indication to a trivalent tensor. The writing of instead of may mean that the writer either is stretched in space (for example, to reduce the publication fees) or aims to increase number of publications without considering readers. The same may apply to any other use of ambiguous notations.
Subscripts are also used to denote the argument to a function, as in .
Examples of potentially confusing ambiguous mathematical expressions[edit]
, which could be understood to mean either or . In addition, may mean , as means (see tetration).
, which by convention means , though it might be thought to mean , since means .
, which arguably should mean but would commonly be understood to mean .
Notations in quantum optics and quantum mechanics[edit]
It is common to define the coherent states in quantum optics with and states with fixed number of photons with . Then, there is an "unwritten rule": the state is coherent if there are more Greek characters than Latin characters in the argument, and photon state if the Latin characters dominate. The ambiguity becomes even worse, if is used for the states with certain value of the coordinate, and means the state with certain value of the momentum, which may be used in books on quantum mechanics. Such ambiguities easily lead to confusions, especially if some normalized adimensional, dimensionless variables are used. Expression may mean a state with single photon, or the coherent state with mean amplitude equal to 1, or state with momentum equal to unity, and so on. The reader is supposed to guess from the context.
Ambiguous terms in physics and mathematics[edit]
Some physical quantities do not yet have established notations; their value (and sometimes even dimension, as in the case of the Einstein coefficients), depends on the system of notations. Many terms are ambiguous. Each use of an ambiguous term should be preceded by the definition, suitable for a specific case. Just like Ludwig Wittgenstein states in Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus: "... Only in the context of a proposition has a name meaning."[4]
A highly confusing term is gain. For example, the sentence "the gain of a system should be doubled", without context, means close to nothing.
It may mean that the ratio of the output voltage of an electric circuit to the input voltage should be doubled.
It may mean that the ratio of the output power of an electric or optical circuit to the input power should be doubled.
It may mean that the gain of the laser medium should be doubled, for example, doubling the population of the upper laser level in a quasi-two level system (assuming negligible absorption of the ground-state).
The term intensity is ambiguous when applied to light. The term can refer to any of irradiance, luminous intensity, radiant intensity, or radiance, depending on the background of the person using the term.
Also, confusions may be related with the use of atomic percent as measure of concentration of a dopant, or resolution of an imaging system, as measure of the size of the smallest detail which still can be resolved at the background of statistical noise. See also Accuracy and precision and its talk.
The Berry paradox arises as a result of systematic ambiguity in the meaning of terms such as "definable" or "nameable". Terms of this kind give rise to vicious circle fallacies. Other terms with this type of ambiguity are: satisfiable, true, false, function, property, class, relation, cardinal, and ordinal.[5]
Mathematical interpretation of ambiguity[edit]
In mathematics and logic, ambiguity can be considered to be an instance of the logical concept of underdetermination—for example, leaves open what the value of X is—while its opposite is a self-contradiction, also called inconsistency, paradoxicalness, or oxymoron, or in mathematics an inconsistent system—such as , which has no solution.
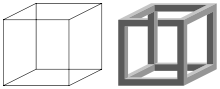
Logical ambiguity and self-contradiction is analogous to visual ambiguity and impossible objects, such as the Necker cube and impossible cube, or many of the drawings of M. C. Escher.[6]
Constructed language[edit]
This section does not cite any sources. (September 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Some languages have been created with the intention of avoiding ambiguity, especially lexical ambiguity. Lojban and Loglan are two related languages which have been created for this, focusing chiefly on syntactic ambiguity as well. The languages can be both spoken and written. These languages are intended to provide a greater technical precision over big natural languages, although historically, such attempts at language improvement have been criticized. Languages composed from many diverse sources contain much ambiguity and inconsistency. The many exceptions to syntax and semantic rules are time-consuming and difficult to learn.
Christianity and Judaiesm[edit]
Christianity and Judaism employ the concept of paradox synonymously with 'ambiguity'. Many Christians and Jews endorse Rudolf Otto's description of the sacred as 'mysterium tremendum et fascinans', the awe-inspiring mystery which fascinates humans.[dubious – discuss] The orthodox Catholic writer G. K. Chesterton regularly employed paradox to tease out the meanings in common concepts which he found ambiguous or to reveal meaning often overlooked or forgotten in common phrases. (The title of one of his most famous books, Orthodoxy, itself employing such a paradox.)
Music[edit]
In music, pieces or sections which confound expectations and may be or are interpreted simultaneously in different ways are ambiguous, such as some polytonality, polymeter, other ambiguous meters or rhythms, and ambiguous phrasing, or (Stein 2005, p. 79) any aspect of music. The music of Africa is often purposely ambiguous. To quote Sir Donald Francis Tovey (1935, p. 195), "Theorists are apt to vex themselves with vain efforts to remove uncertainty just where it has a high aesthetic value."
Visual art[edit]
This section does not cite any sources. (September 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
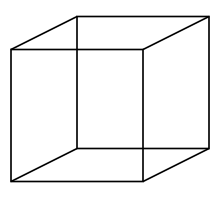
In visual art, certain images are visually ambiguous, such as the Necker cube, which can be interpreted in two ways. Perceptions of such objects remain stable for a time, then may flip, a phenomenon called multistable perception. The opposite of such ambiguous images are impossible objects.
Pictures or photographs may also be ambiguous at the semantic level: the visual image is unambiguous, but the meaning and narrative may be ambiguous: is a certain facial expression one of excitement or fear, for instance?
Computer science[edit]
In computer science, the SI prefixes kilo-, mega- and giga- were historically used in certain contexts to mean either the first three powers of 1024 (1024, 10242 and 10243) contrary to the metric system in which these units unambiguously mean one thousand, one million, and one billion. This usage is particularly prevalent with electronic memory devices (e.g. DRAM) addressed directly by a binary machine register where a decimal interpretation makes no practical sense.
Subsequently, the Ki, Mi, and Gi prefixes were introduced so that binary prefixes could be written explicitly, also rendering k, M, and G unambiguous in texts conforming to the new standard — this led to a new ambiguity in engineering documents lacking outward trace of the binary prefixes (necessarily indicating the new style) as to whether the usage of k, M, and G remains ambiguous (old style) or not (new style). Note also that 1 M (where M is ambiguously 1,000,000 or 1,048,576) is less uncertain than the engineering value 1.0e6 (defined to designate the interval 950,000 to 1,050,000), and that as non-volatile storage devices began to commonly exceed 1 GB in capacity (where the ambiguity begins to routinely impact the second significant digit), GB and TB almost always mean 109 and 1012 bytes.
See also[edit]
- Abbreviation
- Ambiguity (law)
- Ambiguity tolerance
- Amphibology
- Decision problem
- Discrete mathematics
- Disambiguation (disambiguation)
- Double entendre
- Essentially contested concept
- Fallacy
- Formal fallacy
- Golden hammer
- Informal fallacy
- Self reference
- Semantics
- Uncertainty
- Volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity
- Word-sense disambiguation
References[edit]
- ^ "And do you see its long nose and chin? At least, they look exactly like a nose and chin, that is don't they? But they really are two of its legs. You know a Caterpillar has got quantities of legs: you can see more of them, further down." Carroll, Lewis. The Nursery "Alice". Dover Publications (1966), p 27.
- ^ a b Critical Thinking, 10th ed., Ch 3, Moore, Brooke N. and Parker, Richard. McGraw-Hill, 2012
- ^ a b Abramovits, M.; Stegun, I. Handbook on mathematical functions. p. 228.
- ^ Wittgenstein, Ludwig (1999). Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus. Dover Publications Inc. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-486-40445-5.
- ^ Russell/Whitehead, Principia Mathematica
- ^ Goldstein, Laurence (1996). "Reflexivity, Contradiction, Paradox and M. C. Escher". Leonardo. 29 (4): 299–308. doi:10.2307/1576313. JSTOR 1576313
External links[edit]
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Ambiguity |
| Look up ambiguity in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |












![\sin[\alpha]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fbc2f15ca0eea182d50897ea0dd20f60b304622f)