Choke point
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
In military strategy, a choke point (or chokepoint) is a geographical feature on land such as a valley, defile or a bridge or at sea such as a strait, which an armed force is forced to pass, sometimes on a substantially narrower front and therefore greatly decreasing its combat power, to reach its objective. A choke point can allow a numerically inferior defending force to thwart a larger opponent if the attacker cannot bring superior numbers to bear.
Historical examples[edit]
Some historical examples of the tactical use of choke points are King Leonidas I's defense of the Pass of Thermopylae during an invasion led by Xerxes I of Persia; the Battle Of Stamford Bridge in which Harold Godwinson defeated Harald Hardrada; William Wallace's victory over the English at the Battle of Stirling Bridge (Wallace had around 2,300 men against the English army of about 9,000 to 12,000 men and the bridge collapsed during the battle); and the Battle of Agincourt in which Henry V of England decisively defeated the French when they were forced to attack his smaller army through a narrow gap in the Agincourt Woods.
It was the suitability of the Caribbean as a chokepoint that attracted pirates and buccaneers during the 17th century. The Spanish treasure fleets leaving the Americas would need to pass there to pick up the strong, prevailing, westerly winds that would take them back to Spain.
The most important naval choke points were first identified by Fisher in his defence of continued British colonialism (important colonies in parentheses):[1]
- Hormuz Strait between Oman and Iran at the entrance to the Persian Gulf
- Bab-el-Mandeb passage from the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea (Yemen and Socotra)
- Strait of Malacca between Malaysia and Indonesia
- Panama Canal and the Panama Pipeline connecting the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans (British Honduras)
- Suez Canal and the Sumed Pipeline connecting the Red Sea and Mediterranean Sea (Egypt)
- Strait of Gibraltar along the Atlantic Ocean entering the Mediterranean Sea (Spain, Gibraltar and Morocco)
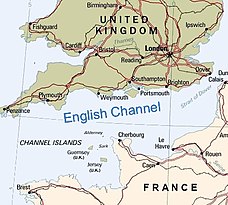
- Strait of Dover or English Channel separating the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea (England and France)
- Strait of Magellan at Cape Horn (Chile)
- The Cape of Good Hope (South Africa)
- Bering Strait (United States of America and Russia)
- Bosporus Strait linking the Black Sea (and oil coming from the Caspian Sea region) to the Mediterranean Sea (Turkey)
- Dardanelles Strait connecting the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean Sea (Turkey)
- Strait of Tartary along Sea of Japan and Sea of Okhotsk (Russia)
The Fulda Gap was seen as one of the potentially decisive bottleneck battlegrounds of the Cold War in Germany.
[edit]
From the 18th to the early 20th centuries, the sheer size of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy meant it had control over much of the world's oceans and seas. Choke points were of huge importance to the British Empire, which often used them to control trade in British colonies and, to a lesser extent, for defense. Choke points have also been a source of tension, notably during the Suez Crisis. The Royal Navy still deems its choke points as strategically vital. Indeed, the importance of choke points was first recognised by British Admiral John Fisher.[1]
These are major British choke points today:
- The English Channel
- GIUK gap (between Greenland, Iceland, and UK)
- Strait of Gibraltar
The choke points still have significant strategic importance for the Royal Navy. The GIUK gap is particularly important to the Royal Navy, as any attempt by northern European forces to break into the open Atlantic would have to do so through the heavily defended English Channel, which is also the world's busiest shipping lane, or through one of the exits on either side of Iceland. Considering British control over the strategic fortress of Gibraltar at the entrance to the Mediterranean, Spain (northern coast), France (Atlantic coast) and Portugal are the only mainland European nations that have direct access to the Atlantic Ocean in a way that cannot be easily blocked at a choke point by the Royal Navy. The GIUK gap was also a strategically important part of the Cold War, as the Royal Navy were given the responsibility of keeping an eye on Soviet submarines trying to break into the open Atlantic.
Importance[edit]
Choke points remain a prominent issue today in the global economy and shipments of goods, particularly oil: 20% of the world's oil is shipped through the Strait of Hormuz, which has seen conflicts such as the downing of Iran Air Flight 655 by American missiles in 1988. The Suez Canal and the Sumed pipeline carry 4.5 million barrels (190,000,000 US gal; 720,000 m3) a day, and the canal carried a total of 7.5% of world trade in 2011.[2] The canal was closed for eight years after the Six-Day War in 1967. In many instances, alternate routes are nonexistent or impractical. For example, an alternate to the Suez/Sumed route required an additional 6,000 miles (9,700 km) around Cape of Good Hope.[3] The Royal Navy also still deems its choke points to the Atlantic as strategically important.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Breverton, Terry (2010). Breverton's Nautical Curiosities. 21 Bloomsbury Square, London: Quercus Publishing PLC. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-84724-776-6.
- ^ "Egypt: Will U.S. And NATO Launch Second Suez Intervention?". Scoop.co.nz. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ^ [1] Archived March 13, 2009, at the Wayback Machine