Portal:Artificial intelligence
Portal maintenance status: (September 2018)
|
Introduction
In the field of computer science, artificial intelligence (AI), sometimes called machine intelligence, is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals. Computer science defines AI research as the study of "intelligent agents": any device that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chance of successfully achieving its goals. More specifically, Kaplan and Haenlein define AI as “a system’s ability to correctly interpret external data, to learn from such data, and to use those learnings to achieve specific goals and tasks through flexible adaptation”. Colloquially, the term "artificial intelligence" is applied when a machine mimics "cognitive" functions that humans associate with other human minds, such as "learning" and "problem solving".
The scope of AI is disputed: as machines become increasingly capable, tasks considered as requiring "intelligence" are often removed from the definition, a phenomenon known as the AI effect, leading to the quip in Tesler's Theorem, "AI is whatever hasn't been done yet." For instance, optical character recognition is frequently excluded from "artificial intelligence", having become a routine technology. Modern machine capabilities generally classified as AI include successfully understanding human speech, competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and Go), autonomously operating cars, and intelligent routing in content delivery networks and military simulations.
Selected general articles
- The ethics of artificial intelligence is the part of the ethics of technology specific to robots and other artificially intelligent beings. It is typically divided into roboethics, a concern with the moral behavior of humans as they design, construct, use and treat artificially intelligent beings, and machine ethics, which is concerned with the moral behavior of artificial moral agents (AMAs). Read more...
- Artificial intelligence, defined as intelligence exhibited by machines, has many applications in today's society. More specifically, it is Weak AI, the form of AI where programs are developed to perform specific tasks, that is being utilized for a wide range of activities including medical diagnosis, electronic trading, robot control, and remote sensing. AI has been used to develop and advance numerous fields and industries, including finance, healthcare, education, transportation, and more. Read more...
A Bayesian network, Bayes network, belief network, decision network, Bayes(ian) model or probabilistic directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model (a type of statistical model) that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases.
Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (e.g. speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Read more...- The Chinese room argument holds that a program cannot give a computer a "mind", "understanding" or "consciousness", regardless of how intelligently or human-like the program may make the computer behave. The argument was first presented by philosopher John Searle in his paper, "Minds, Brains, and Programs", published in Behavioral and Brain Sciences in 1980. It has been widely discussed in the years since. The centerpiece of the argument is a thought experiment known as the Chinese room.
The argument is directed against the philosophical positions of functionalism and computationalism, which hold that the mind may be viewed as an information-processing system operating on formal symbols. Specifically, the argument is intended to refute a position Searle calls Strong AI:
Read more...The appropriately programmed computer with the right inputs and outputs would thereby have a mind in exactly the same sense human beings have minds.
- This is a timeline of artificial intelligence. Read more...
- In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions (see also loss function). Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators.
Evolutionary algorithms often perform well approximating solutions to all types of problems because they ideally do not make any assumption about the underlying fitness landscape. Techniques from evolutionary algorithms applied to the modeling of biological evolution are generally limited to explorations of microevolutionary processes and planning models based upon cellular processes. In most real applications of EAs, computational complexity is a prohibiting factor. In fact, this computational complexity is due to fitness function evaluation. Fitness approximation is one of the solutions to overcome this difficulty. However, seemingly simple EA can solve often complex problems; therefore, there may be no direct link between algorithm complexity and problem complexity. Read more... - A friendly artificial intelligence (also friendly AI or FAI) is a hypothetical artificial general intelligence (AGI) that would have a positive effect on humanity. It is a part of the ethics of artificial intelligence and is closely related to machine ethics. While machine ethics is concerned with how an artificially intelligent agent should behave, friendly artificial intelligence research is focused on how to practically bring about this behaviour and ensuring it is adequately constrained. Read more...
- Knowledge representation and reasoning (KR, KR², KR&R) is the field of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can utilize to solve complex tasks such as diagnosing a medical condition or having a dialog in a natural language. Knowledge representation incorporates findings from psychology about how humans solve problems and represent knowledge in order to design formalisms that will make complex systems easier to design and build. Knowledge representation and reasoning also incorporates findings from logic to automate various kinds of reasoning, such as the application of rules or the relations of sets and subsets.
Examples of knowledge representation formalisms include semantic nets, systems architecture, frames, rules, and ontologies. Examples of automated reasoning engines include inference engines, theorem provers, and classifiers. Read more... - Existential risk from artificial general intelligence is the hypothesis that substantial progress in artificial general intelligence (AGI) could someday result in human extinction or some other unrecoverable global catastrophe. For instance, the human species currently dominates other species because the human brain has some distinctive capabilities that other animals lack. If AI surpasses humanity in general intelligence and becomes "superintelligent", then this new superintelligence could become powerful and difficult to control. Just as the fate of the mountain gorilla depends on human goodwill, so might the fate of humanity depend on the actions of a future machine superintelligence.
The likelihood of this type of scenario is widely debated, and hinges in part on differing scenarios for future progress in computer science. Once the exclusive domain of science fiction, concerns about superintelligence started to become mainstream in the 2010s, and were popularized by public figures such as Stephen Hawking, Bill Gates, and Elon Musk. Read more...  The Shadow robot hand system
The Shadow robot hand system
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and science that includes mechanical engineering, electronic engineering, information engineering, computer science, and others. Robotics deals with the design, construction, operation, and use of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing.
These technologies are used to develop machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations and for lots of purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including bomb detection and deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space). Robots can take on any form but some are made to resemble humans in appearance. This is said to help in the acceptance of a robot in certain replicative behaviors usually performed by people. Such robots attempt to replicate walking, lifting, speech, cognition, and basically anything a human can do. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature, contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. Read more...- Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning or hierarchical learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on learning data representations, as opposed to task-specific algorithms. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
Deep learning architectures such as deep neural networks, deep belief networks and recurrent neural networks have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, audio recognition, social network filtering, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases superior to human experts. Read more... - The following is a list of current and past, nonclassified notable artificial intelligence projects. Read more...
- Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.
This glossary of artificial intelligence terms is about artificial intelligence, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. Read more...  An automated online assistant providing customer service on a web page, an example of an application where natural language processing is a major component.
An automated online assistant providing customer service on a web page, an example of an application where natural language processing is a major component.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science, information engineering, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human (natural) languages, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data.
Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. Read more...- Machine learning (ML) is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to effectively perform a specific task without using explicit instructions, relying on models and inference instead. It is seen as a subset of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a mathematical model of sample data, known as "training data", in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to perform the task. Machine learning algorithms are used in the applications of email filtering, detection of network intruders, and computer vision, where it is infeasible to develop an algorithm of specific instructions for performing the task. Machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predictions using computers. The study of mathematical optimization delivers methods, theory and application domains to the field of machine learning. Data mining is a field of study within machine learning, and focuses on exploratory data analysis through unsupervised learning. In its application across business problems, machine learning is also referred to as predictive analytics. Read more...
Artificial intelligence applications have been used in a wide range of fields including medical diagnosis, stock trading, robot control, law, scientific discovery and toys. However, many AI applications are not perceived as AI: "A lot of cutting edge AI has filtered into general applications, often without being called AI because once something becomes useful enough and common enough it's not labeled AI anymore." "Many thousands of AI applications are deeply embedded in the infrastructure of every industry." In the late 1990s and early 21st century, AI technology became widely used as elements of larger systems, but the field is rarely credited for these successes.
Kaplan and Haenlein structure artificial intelligence along three evolutionary stages: 1) artificial narrow intelligence – applying AI only to specific tasks; 2) artificial general intelligence – applying AI to several areas and able to autonomously solve problems they were never even designed for; and 3) artificial super intelligence – applying AI to any area capable of scientific creativity, social skills, and general wisdom. Read more...- In the history of artificial intelligence, an AI winter is a period of reduced funding and interest in artificial intelligence research. The term was coined by analogy to the idea of a nuclear winter. The field has experienced several hype cycles, followed by disappointment and criticism, followed by funding cuts, followed by renewed interest years or decades later.
The term first appeared in 1984 as the topic of a public debate at the annual meeting of AAAI (then called the "American Association of Artificial Intelligence"). It is a chain reaction that begins with pessimism in the AI community, followed by pessimism in the press, followed by a severe cutback in funding, followed by the end of serious research. At the meeting, Roger Schank and Marvin Minsky—two leading AI researchers who had survived the "winter" of the 1970s—warned the business community that enthusiasm for AI had spiraled out of control in the 1980s and that disappointment would certainly follow. Three years later, the billion-dollar AI industry began to collapse. Read more... - Artificial intelligence researchers have developed several specialized programming languages for artificial intelligence: Read more...
- Automated planning and scheduling, sometimes denoted as simply AI Planning, is a branch of artificial intelligence that concerns the realization of strategies or action sequences, typically for execution by intelligent agents, autonomous robots and unmanned vehicles. Unlike classical control and classification problems, the solutions are complex and must be discovered and optimized in multidimensional space. Planning is also related to decision theory.
In known environments with available models, planning can be done offline. Solutions can be found and evaluated prior to execution. In dynamically unknown environments, the strategy often needs to be revised online. Models and policies must be adapted. Solutions usually resort to iterative trial and error processes commonly seen in artificial intelligence. These include dynamic programming, reinforcement learning and combinatorial optimization. Languages used to describe planning and scheduling are often called action languages. Read more... 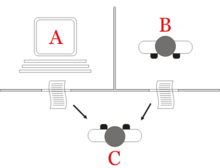 The "standard interpretation" of the Turing test, in which player C, the interrogator, is given the task of trying to determine which player – A or B – is a computer and which is a human. The interrogator is limited to using the responses to written questions to make the determination.
The "standard interpretation" of the Turing test, in which player C, the interrogator, is given the task of trying to determine which player – A or B – is a computer and which is a human. The interrogator is limited to using the responses to written questions to make the determination.
website: http://www.aisb.org.uk/events/loebner-prize
The Turing test, developed by Alan Turing in 1950, is a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. Turing proposed that a human evaluator would judge natural language conversations between a human and a machine designed to generate human-like responses. The evaluator would be aware that one of the two partners in conversation is a machine, and all participants would be separated from one another. The conversation would be limited to a text-only channel such as a computer keyboard and screen so the result would not depend on the machine's ability to render words as speech. If the evaluator cannot reliably tell the machine from the human, the machine is said to have passed the test. The test results do not depend on the machine's ability to give correct answers to questions, only how closely its answers resemble those a human would give.
The test was introduced by Turing in his 1950 paper, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence", while working at the University of Manchester (Turing, 1950; p. 460). It opens with the words: "I propose to consider the question, 'Can machines think?'" Because "thinking" is difficult to define, Turing chooses to "replace the question by another, which is closely related to it and is expressed in relatively unambiguous words." Turing's new question is: "Are there imaginable digital computers which would do well in the imitation game?" This question, Turing believed, is one that can actually be answered. In the remainder of the paper, he argued against all the major objections to the proposition that "machines can think". Read more...- Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can be made to gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to automate tasks that the human visual system can do.
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g., in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images (the input of the retina) into descriptions of the world that can interface with other thought processes and elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. Read more... - Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is the intelligence of a machine that could successfully perform any intellectual task that a human being can. It is a primary goal of some artificial intelligence research and a common topic in science fiction and future studies. Some researchers refer to Artificial general intelligence as "strong AI", "full AI" or as the ability of a machine to perform "general intelligent action"; others reserve "strong AI" for machines capable of experiencing consciousness.
Some references emphasize a distinction between strong AI and "applied AI" (also called "narrow AI" or "weak AI"): the use of software to study or accomplish specific problem solving or reasoning tasks. Weak AI, in contrast to strong AI, does not attempt to perform the full range of human cognitive abilities. Read more...
Did you know...
- ... that Prisma uses a neural network and artificial intelligence to edit pictures?
- ... that data from Media Bias/Fact Check was used to train an artificial intelligence machine learning algorithm to identify fake news?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Artificial intelligence that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Artificial intelligence-related articles, see WikiProject Artificial intelligence.
Selected images
The word "robot" itself was coined by Karel Čapek in his 1921 play R.U.R., the title standing for "Rossum's Universal Robots"
A parse tree represents the syntactic structure of a sentence according to some formal grammar.
Kismet, a robot with rudimentary social skills
An automated online assistant providing customer service on a web page – one of many very primitive applications of artificial intelligence
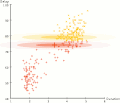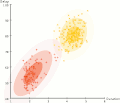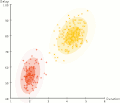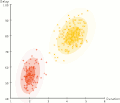
Expectation-maximization clustering of Old Faithful eruption data starts from a random guess but then successfully converges on an accurate clustering of the two physically distinct modes of eruption.
Feature detection (pictured: edge detection) helps AI compose informative abstract structures out of raw data.
A patient-side surgical arm of Da Vinci Surgical System
A particle swarm seeking the global minimum
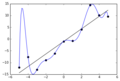
The blue line could be an example of overfitting a linear function due to random noise.
A hierarchical control system is a form of control system in which a set of devices and governing software is arranged in a hierarchy.
A neural network is an interconnected group of nodes, akin to the vast network of neurons in the human brain.
Subcategories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikibooks
Books
Commons
Media
Wikinews
News
Wikiquote
Quotations
Wikisource
Texts
Wikiversity
Learning resources
Wiktionary
Definitions
Wikidata
Database
- What are portals?
- List of portals