Portal:Analytic philosophy
Portal maintenance status: (September 2018)
|
Introduction
Analytic philosophy (sometimes analytical philosophy) is a style of philosophy that became dominant in the Western world at the beginning of the 20th century. The term can refer to one of several things:
- As a philosophical practice, it is characterized by an emphasis on argumentative clarity and precision, often making use of formal logic, conceptual analysis, and, to a lesser degree, mathematics and the natural sciences.
- As a historical development, analytic philosophy refers to certain developments in early 20th-century philosophy that were the historical antecedents of the current practice. Central figures in this historical development are Bertrand Russell, Ludwig Wittgenstein, G.E. Moore, Gottlob Frege, and the logical positivists. In this more specific sense, analytic philosophy is identified with specific philosophical traits (many of which are rejected by many contemporary analytic philosophers), such as:
- The logical-positivist principle that there are not any specifically philosophical facts and that the object of philosophy is the logical clarification of thoughts. This may be contrasted with the traditional foundationalism, which considers philosophy to be a special science (i.e., the discipline of knowledge) that investigates the fundamental reasons and principles of everything. Consequently, many analytic philosophers have considered their inquiries as continuous with, or subordinate to, those of the natural sciences. This is an attitude that begins with John Locke, who described his work as that of an "underlabourer" to the achievements of natural scientists such as Newton. During the 20th century, the most influential advocate of the continuity of philosophy with science was Willard Van Orman Quine.
- The principle that the logical clarification of thoughts can be achieved only by analysis of the logical form of philosophical propositions. The logical form of a proposition is a way of representing it (often using the formal grammar and symbolism of a logical system), to reduce it to simpler components if necessary, and to display its similarity with all other propositions of the same type. However, analytic philosophers disagree widely about the correct logical form of ordinary language.
- The neglect of generalized philosophical systems in favour of more restricted inquiries stated rigorously, or ordinary language.
According to a characteristic paragraph by Russell:
Modern analytical empiricism [...] differs from that of Locke, Berkeley, and Hume by its incorporation of mathematics and its development of a powerful logical technique. It is thus able, in regard to certain problems, to achieve definite answers, which have the quality of science rather than of philosophy. It has the advantage, in comparison with the philosophies of the system-builders, of being able to tackle its problems one at a time, instead of having to invent at one stroke a block theory of the whole universe. Its methods, in this respect, resemble those of science.
Selected general articles
- In the philosophy of perception, the theory of sense data was a popular view held in the early 20th century by philosophers such as Bertrand Russell, C. D. Broad, H. H. Price, A. J. Ayer, and G. E. Moore. Sense data are taken to be mind-dependent objects whose existence and properties are known directly to us in perception. These objects are unanalyzed experiences inside the mind, which appear to subsequent more advanced mental operations exactly as they are.
Sense data are often placed in a time and/or causality series, such that they occur after the potential unreliability of our perceptual systems yet before the possibility of error during higher-level conceptual analysis and are thus incorrigible. They are thus distinct from the 'real' objects in the world outside the mind, about whose existence and properties we often can be mistaken. Read more... - Thomas Samuel Kuhn (/kuːn/; July 18, 1922 – June 17, 1996) was an American physicist, historian and philosopher of science whose controversial 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions was influential in both academic and popular circles, introducing the term paradigm shift, which has since become an English-language idiom.
Kuhn made several notable claims concerning the progress of scientific knowledge: that scientific fields undergo periodic "paradigm shifts" rather than solely progressing in a linear and continuous way, and that these paradigm shifts open up new approaches to understanding what scientists would never have considered valid before; and that the notion of scientific truth, at any given moment, cannot be established solely by objective criteria but is defined by a consensus of a scientific community. Competing paradigms are frequently incommensurable; that is, they are competing and irreconcilable accounts of reality. Thus, our comprehension of science can never rely wholly upon "objectivity" alone. Science must account for subjective perspectives as well, since all objective conclusions are ultimately founded upon the subjective conditioning/worldview of its researchers and participants. Read more...
William Lane Craig (born August 23, 1949) is an American analytic philosopher and Christian theologian. He holds faculty positions at Talbot School of Theology (Biola University) and Houston Baptist University. Craig has developed and defended the Kalam cosmological argument for the existence of God. He also focused in his published work on a historical argument for the resurrection of Jesus. His research on divine aseity and Platonism culminated with his book God Over All. He has also debated the existence of God with public figures such as Sam Harris, Christopher Hitchens, Lawrence M. Krauss and A. C. Grayling. Craig established and runs the online apologetics ministry ReasonableFaith.org. Read more...- Frank Plumpton Ramsey (/ˈræmzi/; 22 February 1903 – 19 January 1930) was a British philosopher, mathematician and economist who made major contributions to all three fields before his death at the age of 26. He was a close friend of Ludwig Wittgenstein and was instrumental in translating Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus into English, as well as persuading Wittgenstein to return to philosophy and Cambridge. Like Wittgenstein, he was a member of the Cambridge Apostles, the intellectual secret society, from 1921. Read more...
John Henry McDowell (born 7 March 1942) is a South African philosopher, formerly a fellow of University College, Oxford and now University Professor at the University of Pittsburgh. Although he has written extensively on metaphysics, epistemology, ancient philosophy, and meta-ethics, McDowell's most influential work has been in the philosophy of mind and philosophy of language. McDowell was one of three recipients of the 2010 Andrew W. Mellon Foundation's Distinguished Achievement Award. and is a Fellow of both the American Academy of Arts & Sciences and the British Academy.
McDowell has, throughout his career, understood philosophy to be "therapeutic" and thereby to "leave everything as it is", which he understands to be a form of philosophical quietism (although he does not consider himself to be a "quietist"). The philosophical quietist believes that philosophy cannot make any explanatory comment about how, for example, thought and talk relate to the world but can, by offering re-descriptions of philosophically problematic cases, return the confused philosopher to a state of intellectual quietude. However, in defending this quietistic perspective McDowell has engaged with the work of leading contemporaries in such a way as to therapeutically dissolve what he takes to be philosophical error, while developing original and distinctive theses about language, mind and value. In each case, he has tried to resist the influence of what he regards as a misguided, reductive form of philosophical naturalism that dominates the work of his contemporaries, particularly in North America. Read more...- Sir Bernard Arthur Owen Williams, FBA (21 September 1929 – 10 June 2003) was an English moral philosopher. His publications include Problems of the Self (1973), Ethics and the Limits of Philosophy (1985), Shame and Necessity (1993), and Truth and Truthfulness (2002). He was knighted in 1999.
As Knightbridge Professor of Philosophy at the University of Cambridge and Deutsch Professor of Philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley, Williams became known for his efforts to reorient the study of moral philosophy to psychology, history, and in particular to the Greeks. Described by Colin McGinn as an "analytical philosopher with the soul of a general humanist," he was sceptical about attempts to create a foundation for moral philosophy. Martha Nussbaum wrote that he demanded of philosophy that it "come to terms with, and contain, the difficulty and complexity of human life." Read more... - Ernest Nagel (November 16, 1901 – September 20, 1985) was an American philosopher of science. Along with Rudolf Carnap, Hans Reichenbach, and Carl Hempel, he is sometimes seen as one of the major figures of the logical positivist movement. Read more...
- Sir Alfred Jules "Freddie" Ayer FBA (/ɛər/; 29 October 1910 – 27 June 1989), usually cited as A. J. Ayer, was a British philosopher known for his promotion of logical positivism, particularly in his books Language, Truth, and Logic (1936) and The Problem of Knowledge (1956).
He was educated at Eton College and Oxford University, after which he studied the philosophy of logical positivism at the University of Vienna. From 1933 to 1940 he lectured on philosophy at Christ Church, Oxford. Read more... - Keith Sedgwick Donnellan (/ˈdɒnələn/; 25 June 1931 – 20 February 2015) was an American philosopher and Professor Emeritus of the UCLA department of Philosophy. He spent most of his career at UCLA but taught, before that, at Cornell, where he also earned his PhD. Donnellan contributed to the philosophy of language, most notably to the analysis of proper names and definite descriptions. For instance, Donnellan criticized Bertrand Russell's theory of definite descriptions for overlooking the distinction between referential and attributive use of definite descriptions. Read more...
- Neurophilosophy or philosophy of neuroscience is the interdisciplinary study of neuroscience and philosophy that explores the relevance of neuroscientific studies to the arguments traditionally categorized as philosophy of mind. The philosophy of neuroscience attempts to clarify neuroscientific methods and results using the conceptual rigor and methods of philosophy of science. Read more...
- Neopragmatism, sometimes called post-Deweyan pragmatism, linguistic pragmatism, or analytic pragmatism, is the philosophical tradition that infers that the meaning of words is a function of how they are used, rather than the meaning of what people intend for them to describe.
The Blackwell Dictionary of Western Philosophy (2004) defines "neo-pragmatism" as "A postmodern version of pragmatism developed by the American philosopher Richard Rorty and drawing inspiration from authors such as John Dewey, Martin Heidegger, Wilfrid Sellars, Quine, and Jacques Derrida". It's a contemporary term for a philosophy which reintroduces many concepts from pragmatism. While traditional pragmatism focuses on experience, Rorty centers on language. The self is regarded as a "centerless web of beliefs and desires". Read more... - John Langshaw Austin (26 March 1911 – 8 February 1960) was a British philosopher of language and leading proponent of ordinary language philosophy, perhaps best known for developing the theory of speech acts.
Austin pointed out that we use language to do things as well as to assert things, and that the utterance of a statement like "I promise to do so-and-so" is best understood as doing something — making a promise — rather than making an assertion about anything. Hence the name of one of his best-known works How to Do Things with Words. Austin, in providing his theory of speech acts, makes a significant challenge to the philosophy of language, far beyond merely elucidating a class of morphological sentence forms that function to do what they name. Austin's work ultimately suggests that all speech and all utterance is the doing of something with words and signs, challenging a metaphysics of language that would posit denotative, propositional assertion as the essence of language and meaning. Read more... - Sir Peter Frederick Strawson FBA (/ˈstrɔːsən/; 23 November 1919 – 13 February 2006), usually cited as P. F. Strawson, was an English philosopher. He was the Waynflete Professor of Metaphysical Philosophy at the University of Oxford (Magdalen College) from 1968 to 1987. Before that, he was appointed as a college lecturer at University College, Oxford, in 1947, and became a tutorial fellow the following year, until 1968. On his retirement in 1987, he returned to the college and continued working there until shortly before his death. His portrait was painted by the artists Muli Tang and Daphne Todd.
When he died, the obituary in The Guardian noted that, "Oxford was the world capital of philosophy between 1950 and 1970, and American academics flocked there, rather than the traffic going the other way. That golden age had no greater philosopher than Sir Peter Strawson." Read more... - Modal realism is the view propounded by David Kellogg Lewis that all possible worlds are real in the same way as is the actual world: they are "of a kind with this world of ours." It is based on the following tenets: possible worlds exist; possible worlds are not different in kind from the actual world; possible worlds are irreducible entities; the term actual in actual world is indexical, i.e. any subject can declare their world to be the actual one, much as they
label the place they are "here" and the time they are "now". Read more...
Saul Aaron Kripke (/sɔːlˈkrɪpki/ ; born November 13, 1940) is an American philosopher and logician. He is a Distinguished Professor of Philosophy at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York and emeritus professor at Princeton University. Since the 1960s, Kripke has been a central figure in a number of fields related to mathematical logic, philosophy of language, philosophy of mathematics, metaphysics, epistemology, and set theory. Much of his work remains unpublished or exists only as tape recordings and privately circulated manuscripts. Kripke was the recipient of the 2001 Schock Prize in Logic and Philosophy.
Kripke has made influential and original contributions to logic, especially modal logic. His work has profoundly influenced analytic philosophy; his principal contribution is a semantics for modal logic involving possible worlds, now called Kripke semantics. Another of his most important contributions is his argument that necessity is a "metaphysical" notion that should be separated from the epistemic notion of a priori, and that there are necessary truths that are a posteriori truths, such as that water is H2O. He has also contributed an original reading of Wittgenstein, referred to as "Kripkenstein." A 1970 Princeton lecture series, published in book form in 1980 as Naming and Necessity, is considered one of the most important philosophical works of the twentieth century. Read more...- David Kellogg Lewis (September 28, 1941 – October 14, 2001) was an American philosopher. Lewis taught briefly at UCLA and then at Princeton from 1970 until his death. He is also closely associated with Australia, whose philosophical community he visited almost annually for more than thirty years. He made contributions in philosophy of language, philosophy of mind, philosophy of probability, metaphysics, epistemology, philosophical logic, and aesthetics. He is probably best known for his controversial modal realist stance: that (i) possible worlds exist, (ii) every possible world is a concrete entity, (iii) any possible world is causally and spatiotemporally isolated from any other possible world, and (iv) our world is among the possible worlds. Read more...
Antony Garrard Newton Flew (/fluː/; 11 February 1923 – 8 April 2010) was an English philosopher. Belonging to the analytic and evidentialist schools of thought, Flew was most notable for his work related to the philosophy of religion. During the course of his career he taught at the universities of Oxford, Aberdeen, Keele and Reading, and at York University in Toronto.
For much of his career Flew was known as a strong advocate of atheism, arguing that one should presuppose atheism until empirical evidence of a God surfaces. He also criticised the idea of life after death, the free will defence to the problem of evil, and the meaningfulness of the concept of God. In 2003 he was one of the signatories of the Humanist Manifesto III. Read more...
Michael Laban Walzer (/ˈwɔːlzər/; born 1935) is a prominent American political theorist and public intellectual. A professor emeritus at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey, he is co-editor of Dissent, an intellectual magazine that he has been affiliated with since his years as an undergraduate at Brandeis University. He has written books and essays on a wide range of topics—many in political ethics—including just and unjust wars, nationalism, ethnicity, Zionism, economic justice, social criticism, radicalism, tolerance, and political obligation. He is also a contributing editor to The New Republic. To date, he has written 27 books and published over 300 articles, essays, and book reviews in Dissent, The New Republic, The New York Review of Books, The New Yorker, The New York Times, Harpers, and many philosophical and political science journals. Read more...
Sir Michael Anthony Eardley Dummett, FBA (/ˈdʌmɪt/; 27 June 1925 – 27 December 2011) was an English academic described as "among the most significant British philosophers of the last century and a leading campaigner for racial tolerance and equality." He was, until 1992, Wykeham Professor of Logic at the University of Oxford. He wrote on the history of analytic philosophy, notably as an interpreter of Frege, and made original contributions particularly in the philosophies of mathematics, logic, language and metaphysics. He was known for his work on truth and meaning and their implications to debates between realism and anti-realism, a term he helped to popularize. He devised the Quota Borda system of proportional voting, based on the Borda count. In mathematical logic, he developed an intermediate logic, already studied by Kurt Gödel: the Gödel–Dummett logic. Read more...
Sir Karl Raimund Popper CH FBA FRS (28 July 1902 – 17 September 1994) was an Austrian-British philosopher and professor.
Generally regarded as one of the 20th century's greatest philosophers of science, Popper is known for his rejection of the classical inductivist views on the scientific method in favour of empirical falsification. A theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified, meaning that it can and should be scrutinised by decisive experiments. Popper is also known for his opposition to the classical justificationist account of knowledge, which he replaced with critical rationalism, namely "the first non-justificational philosophy of criticism in the history of philosophy". Read more...- George Edward Moore OM FBA (4 November 1873 – 24 October 1958) was an English philosopher. He was, with Bertrand Russell, Ludwig Wittgenstein, and (before them) Gottlob Frege, one of the founders of the analytic tradition in philosophy. Along with Russell, he led the turn away from idealism in British philosophy, and became well known for his advocacy of common sense concepts, his contributions to ethics, epistemology, and metaphysics, and "his exceptional personality and moral character". He was Professor of Philosophy at the University of Cambridge, highly influential among (though not a member of) the Bloomsbury Group, and the editor of the influential journal Mind. He was elected a fellow of the British Academy in 1918. He was a member of the Cambridge Apostles, the intellectual secret society, from 1894 to 1901, and the Cambridge University Moral Sciences Club. Read more...
Alvin Carl Plantinga (/ˈplæntɪŋɡə/; born November 15, 1932) is a prominent American analytic philosopher who works primarily in the fields of logic, justification, philosophy of religion, and epistemology.
From 1963-82, Plantinga taught at Calvin College before accepting an appointment as the John A. O'Brien Professor of Philosophy at the University of Notre Dame. He later returned to Calvin College to become the inaugural holder of the Jellema Chair in Philosophy. Read more...
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, political activist, and social critic. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He holds a joint appointment as Institute Professor Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and laureate professor at the University of Arizona, and is the author of over 100 books on topics such as linguistics, war, politics, and mass media. Ideologically, he aligns with anarcho-syndicalism and libertarian socialism.
Born to middle-class Ashkenazi Jewish immigrants in Philadelphia, Chomsky developed an early interest in anarchism from alternative bookstores in New York City. He began studying at the University of Pennsylvania at age 16, taking courses in linguistics, mathematics, and philosophy. From 1951 to 1955, he was appointed to Harvard University's Society of Fellows. While at Harvard, he developed the theory of transformational grammar; for this, he was awarded his doctorate in 1955. Chomsky began teaching at MIT in 1957 and emerged as a significant figure in the field of linguistics for his landmark work Syntactic Structures, which remodelled the scientific study of language. From 1958 to 1959, he was a National Science Foundation fellow at the Institute for Advanced Study. Chomsky is credited as the creator or co-creator of the universal grammar theory, the generative grammar theory, the Chomsky hierarchy, and the minimalist program. He also played a pivotal role in the decline of behaviorism, being particularly critical of the work of B. F. Skinner. Read more...- In analytic philosophy, anti-realism is an epistemological position first articulated by British philosopher Michael Dummett. The term was coined as an argument against a form of realism Dummett saw as 'colorless reductionism'.
In anti-realism, the truth of a statement rests on its demonstrability through internal logic mechanisms, such as the context principle or intuitionistic logic, in direct opposition to the realist notion that the truth of a statement rests on its correspondence to an external, independent reality. In anti-realism, this external reality is hypothetical and is not assumed. Read more... - Non-classical logics (and sometimes alternative logics) are formal systems that differ in a significant way from standard logical systems such as propositional and predicate logic. There are several ways in which this is done, including by way of extensions, deviations, and variations. The aim of these departures is to make it possible to construct different models of logical consequence and logical truth.
Philosophical logic is understood to encompass and focus on non-classical logics, although the term has other meanings as well. In addition, some parts of theoretical computer science can be thought of as using non-classical reasoning, although this varies according to the subject area. For example, the basic boolean functions (e.g. AND, OR, NOT, etc) in computer science are very much classical in nature, as is clearly the case given the fact that they can be fully described by classical truth tables. However, in contrast, some computerized proof methods may not use classical logic in the reasoning process. Read more...
Paul Karl Feyerabend (/ˈfaɪərˌæbənd/; German: [ˈfaɪɐˌʔaːbn̩t, -ˌʔaːbm̩t]; January 13, 1924 – February 11, 1994) was an Austrian-born philosopher of science best known for his work as a professor of philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley, where he worked for three decades (1958–1989). At various different points in his life, he lived in England, the United States, New Zealand, Italy, Germany, and finally Switzerland. His major works include Against Method (published in 1975), Science in a Free Society (published in 1978) and Farewell to Reason (a collection of papers published in 1987). Feyerabend became famous for his purportedly anarchistic view of science and his rejection of the existence of universal methodological rules. He was an influential figure in the sociology of scientific knowledge. Asteroid (22356) Feyerabend is named in his honour. Read more...
Peter Albert David Singer, AC (born 6 July 1946) is an Australian moral philosopher. He is the Ira W. DeCamp Professor of Bioethics at Princeton University, and a Laureate Professor at the Centre for Applied Philosophy and Public Ethics at the University of Melbourne. He specialises in applied ethics and approaches ethical issues from a secular, utilitarian perspective. He is known in particular for his book Animal Liberation (1975), in which he argues in favour of veganism, and his essay "Famine, Affluence, and Morality", in which he argues in favour of donating to help the global poor. For most of his career, he was a preference utilitarian, but he stated in The Point of View of the Universe (2014), coauthored with Katarzyna de Lazari-Radek, that he had become a hedonistic utilitarian.
On two occasions, Singer served as chair of the philosophy department at Monash University, where he founded its Centre for Human Bioethics. In 1996 he stood unsuccessfully as a Greens candidate for the Australian Senate. In 2004 Singer was recognised as the Australian Humanist of the Year by the Council of Australian Humanist Societies. In 2005, the Sydney Morning Herald placed him among Australia's ten most influential public intellectuals. Singer is a cofounder of Animals Australia and the founder of The Life You Can Save. Read more...- Herbert Paul Grice (13 March 1913 – 28 August 1988), usually publishing under the name H. P. Grice, H. Paul Grice, or Paul Grice, was a British philosopher of language, whose work on meaning has influenced the philosophical study of semantics. He is known for his theory of implicature. Read more...
Daniel Clement Dennett III (born March 28, 1942) is an American philosopher, writer, and cognitive scientist whose research centers on the philosophy of mind, philosophy of science, and philosophy of biology, particularly as those fields relate to evolutionary biology and cognitive science.
As of 2017, he is the co-director of the Center for Cognitive Studies and the Austin B. Fletcher Professor of Philosophy at Tufts University. Dennett is an atheist and secularist, a member of the Secular Coalition for America advisory board, and a member of the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry, as well as an outspoken supporter of the Brights movement. Dennett is referred to as one of the "Four Horsemen of New Atheism", along with Richard Dawkins, Sam Harris, and the late Christopher Hitchens. Read more...- Donald Herbert Davidson (March 6, 1917 – August 30, 2003) was an American philosopher. He served as Slusser Professor of Philosophy at the University of California, Berkeley from 1981 to 2003 after having also held teaching appointments at Stanford University, Rockefeller University, Princeton University, and the University of Chicago. Davidson was known for his charismatic personality and the depth and difficulty of his thought. His work exerted considerable influence in many areas of philosophy from the 1960s onward, particularly in philosophy of mind, philosophy of language, and action theory. While Davidson was an analytic philosopher, and most of his influence lies in that tradition, his work has attracted attention in continental philosophy as well, particularly in literary theory and related areas.
Although published mostly in the form of short, terse essays that do not explicitly rely on any overriding theory, his work is nonetheless noted for a highly unified character, the same methods and ideas brought to bear on a host of apparently unrelated problems, and for synthesizing the work of a great number of other philosophers. He developed an influential truth-conditional semantics, attacked the idea of mental events as governed by strict psychological laws, and rejected the conception of linguistic understanding as having to do with conventions or rules, concluding famously that "there is no such thing as a language, not if a language is anything like what many philosophers and linguists have supposed. There is therefore no such thing to be learned, mastered, or born with." His philosophical work, as a whole, is said to be concerned with how human beings communicate and interact with one another. Read more...
Graham Priest (born 1948) is Distinguished Professor of Philosophy at the CUNY Graduate Center, as well as a regular visitor at the University of Melbourne where he was Boyce Gibson Professor of Philosophy and also at the University of St Andrews. Read more... Searle at Christ Church, Oxford, 2005
Searle at Christ Church, Oxford, 2005
John Rogers Searle (/sɜːrl/; born 31 July 1932) is an American philosopher. He is currently Willis S. and Marion Slusser Professor Emeritus of the Philosophy of Mind and Language and Professor of the Graduate School at the University of California, Berkeley. Widely noted for his contributions to the philosophy of language, philosophy of mind, and social philosophy, he began teaching at UC Berkeley in 1959.
As an undergraduate at the University of Wisconsin, Searle was secretary of "Students against Joseph McCarthy". He received all his university degrees, BA, MA, and DPhil, from the University of Oxford, where he held his first faculty positions. Later, at UC Berkeley, he became the first tenured professor to join the 1964–1965 Free Speech Movement. In the late 1980s, Searle challenged the restrictions of Berkeley's 1980 rent stabilization ordinance. Following what came to be known as the California Supreme Court's "Searle Decision" of 1990, Berkeley changed its rent control policy, leading to large rent increases between 1991 and 1994. Read more...
Hans Reichenbach (September 26, 1891 – April 9, 1953) was a leading philosopher of science, educator, and proponent of logical empiricism. He was influential in the areas of science, education, and of logical empiricism. He founded the Gesellschaft für empirische Philosophie (Society for Empirical Philosophy) in Berlin in 1928, also known as the “Berlin Circle”. Carl Gustav Hempel, Richard von Mises, David Hilbert and Kurt Grelling all became members of the Berlin Circle. He authored The Rise of Scientific Philosophy. In 1930, Reichenbach and Rudolf Carnap became editors of the journal Erkenntnis (Knowledge). He also made lasting contributions to the study of empiricism based on a theory of probability; the logic and the philosophy of mathematics; space, time, and relativity theory; analysis of probabilistic reasoning; and quantum mechanics. Read more...
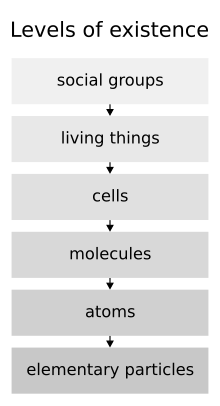
In philosophy, supervenience refers to a relation between sets of properties or sets of facts. X is said to supervene on Y if and only if some difference in Y is necessary for any difference in X to be possible. Equivalently, X is said to supervene on Y if and only if X cannot vary unless Y varies. Here are some examples.- Whether there is a table in the living room supervenes on the positions of molecules in the living room.
- The truth value of (A) supervenes on the truth value of (¬A).
- Molecular properties supervene on atomic properties.
- The quality of Nixon’s moral character supervenes on how he is disposed to act.
- Analysis is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (384–322 B.C.), though analysis as a formal concept is a relatively recent development.
The word comes from the Ancient Greek ἀνάλυσις (analysis, "a breaking up", from ana- "up, throughout" and lysis "a loosening"). Read more...
Alice Crary (/ˈkrɛəri/; born 1967) is an American philosopher who is Professor of Philosophy at the University of Oxford and also at the Graduate Faculty, The New School for Social Research in New York City, where she was the Philosophy Department Chair 2014-17 and founding Co-Chair of the Gender and Sexuality Studies program. For the academic year 2017-18, she was a Member of the School of Social Science at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. In the summer 2018 she was LFUI-Wittgenstein Guest Professor at the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
Crary has influenced a generation of philosophy students at both graduate and undergraduate levels, and was named one of the three "most inspirational" professors at The New School, above all for "path-breaking work...as Chair to bring about greater inclusiveness among populations traditionally under-represented in philosophy." Read more...- The philosophy of mathematics is the branch of philosophy that studies the assumptions, foundations, and implications of mathematics, and purports to provide a viewpoint of the nature and methodology of mathematics, and to understand the place of mathematics in people's lives. The logical and structural nature of mathematics itself makes this study both broad and unique among its philosophical counterparts. Read more...
- Carl Gustav "Peter" Hempel (January 8, 1905 – November 9, 1997) was a German writer and philosopher. He was a major figure in logical empiricism, a 20th-century movement in the philosophy of science. He is especially well known for his articulation of the deductive-nomological model of scientific explanation, which was considered the "standard model" of scientific explanation during the 1950s and 1960s. He is also known for the raven paradox (also known as "Hempel's paradox"). Read more...
- Rudolf Carnap (/ˈkɑːrnæp/; German: [ˈkaɐ̯naːp]; May 18, 1891 – September 14, 1970) was a German-born philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a major member of the Vienna Circle and an advocate of logical positivism. He is considered "one of the giants among twentieth-century philosophers." Read more...
- Australian realism, also called Australian materialism, is a school of philosophy that flourished in the first half of the 20th century in several universities in Australia including the Australian National University, the University of Adelaide, and the University of Sydney, and whose central claim, as stated by leading theorist John Anderson, was that "whatever exists … is real, that is to say it is a spatial and temporal situation or occurrence that is on the same level of reality as anything else that exists". Coupled with this was Anderson's idea that "every fact (which includes every “object”) is a complex situation: there are no simples, no atomic facts, no objects which cannot be, as it were, expanded into facts." Prominent players included Anderson, David Malet Armstrong, J. L. Mackie, Ullin Place, J. J. C. Smart, and David Stove. The label "Australian realist" was conferred on acolytes of Anderson by A. J. Baker in 1986, to mixed approval from those realist philosophers who happened to be Australian. David Malet Armstrong "suggested, half-seriously, that 'the strong sunlight and harsh brown landscape of Australia force reality upon us'". Read more...
Nick Bostrom (/ˈbɒstrəm/; Swedish: Niklas Boström [²buːstrœm]; born 10 March 1973) is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk, the anthropic principle, human enhancement ethics, superintelligence risks, and the reversal test. In 2011, he founded the Oxford Martin Programme on the Impacts of Future Technology, and he is currently the founding director of the Future of Humanity Institute at Oxford University.
Bostrom is the author of over 200 publications, including Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies (2014), a New York Times bestseller and Anthropic Bias: Observation Selection Effects in Science and Philosophy (2002). In 2009 and 2015, he was included in Foreign Policy's Top 100 Global Thinkers list. Bostrom believes there are potentially great benefits from Artificial General Intelligence, but warns it might very quickly transform into a superintelligence that would deliberately extinguish humanity out of precautionary self-preservation or some unfathomable motive, making solving the problems of control beforehand an absolute priority. Although his book on superintelligence was recommended by both Elon Musk and Bill Gates, Bostrom has expressed frustration that the reaction to its thesis typically falls into two camps, one calling his recommendations absurdly alarmist because creation of superintelligence is unfeasible, and the other deeming them futile because superintelligence would be uncontrollable. Bostrom notes that both these lines of reasoning converge on inaction rather than trying to solve the control problem while there may still be time. Read more...
David John Chalmers (/ˈtʃælmərz/; born 20 April 1966) is an Australian philosopher and cognitive scientist specializing in the areas of philosophy of mind and philosophy of language. He is Professor of Philosophy and Director of the Centre for Consciousness at the Australian National University. He is also a University Professor, Professor of Philosophy and Neural Science, and a Director of the Center for Mind, Brain and Consciousness (along with Ned Block) at New York University. In 2013, he was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. Read more...
Charles Margrave Taylor CC GOQ FBA FRSC (born 1931) is a Canadian philosopher from Montreal, Quebec, and professor emeritus at McGill University best known for his contributions to political philosophy, the philosophy of social science, the history of philosophy, and intellectual history. This work has earned him the Kyoto Prize, the Templeton Prize, the Berggruen Prize for Philosophy, and the John W. Kluge Prize.
In 2007, Taylor served with Gérard Bouchard on the Bouchard–Taylor Commission on reasonable accommodation with regard to cultural differences in the province of Quebec. He has also made contributions to moral philosophy, epistemology, hermeneutics, aesthetics, the philosophy of mind, the philosophy of language, and the philosophy of action. Read more...
Ian MacDougall Hacking (born February 18, 1936) is a Canadian philosopher specializing in the philosophy of science. Throughout his career, he has won numerous awards, such as the Killam Prize for the Humanities and the Balzan Prize, and been a member of many prestigious groups, including the Order of Canada, the Royal Society of Canada and the British Academy. Read more...- John Jamieson Carswell "Jack" Smart AC (16 September 1920 – 6 October 2012) was an Australian philosopher and academic, and was appointed as an Emeritus Professor by the Australian National University. He worked in the fields of metaphysics, philosophy of science, philosophy of mind, philosophy of religion, and political philosophy. He wrote multiple entries for the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Read more...
Willard Van Orman Quine (/kwaɪn/; known to intimates as "Van"; June 25, 1908 – December 25, 2000) was an American philosopher and logician in the analytic tradition, recognized as "one of the most influential philosophers of the twentieth century." From 1930 until his death 70 years later, Quine was continually affiliated with Harvard University in one way or another, first as a student, then as a professor of philosophy and a teacher of logic and set theory, and finally as a professor emeritus who published or revised several books in retirement. He filled the Edgar Pierce Chair of Philosophy at Harvard from 1956 to 1978. A 2009 poll conducted among analytic philosophers named Quine as the fifth most important philosopher of the past two centuries. He won the first Schock Prize in Logic and Philosophy in 1993 for "his systematical and penetrating discussions of how learning of language and communication are based on socially available evidence and of the consequences of this for theories on knowledge and linguistic meaning." In 1996 he was awarded the Kyoto Prize in Arts and Philosophy for his "outstanding contributions to the progress of philosophy in the 20th century by proposing numerous theories based on keen insights in logic, epistemology, philosophy of science and philosophy of language."
Quine falls squarely into the analytic philosophy tradition while also being the main proponent of the view that philosophy is not conceptual analysis but the abstract branch of the empirical sciences. His major writings include Two Dogmas of Empiricism (1951), which attacked the distinction between analytic and synthetic propositions and advocated a form of semantic holism, and Word and Object (1960), which further developed these positions and introduced Quine's famous indeterminacy of translation thesis, advocating a behaviorist theory of meaning. He also developed an influential naturalized epistemology that tried to provide "an improved scientific explanation of how we have developed elaborate scientific theories on the basis of meager sensory input." He is also important in philosophy of science for his "systematic attempt to understand science from within the resources of science itself" and for his conception of philosophy as continuous with science. This led to his famous quip that "philosophy of science is philosophy enough." In philosophy of mathematics, he and his Harvard colleague Hilary Putnam developed the "Quine–Putnam indispensability thesis," an argument for the reality of mathematical entities. Read more...
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege (/ˈfreɪɡə/; German: [ˈɡɔtloːp ˈfreːɡə]; 8 November 1848 – 26 July 1925) was a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician. He is understood by many to be the father of analytic philosophy, concentrating on the philosophy of language and mathematics. Though largely ignored during his lifetime, Giuseppe Peano (1858–1932) and Bertrand Russell (1872–1970) introduced his work to later generations of logicians and philosophers.
His contributions include the development of modern logic in the Begriffsschrift and work in the foundations of mathematics. His book the Foundations of Arithmetic is the seminal text of the logicist project, and is cited by Michael Dummett as where to pinpoint the linguistic turn. His philosophical papers "On Sense and Reference" ("Über Sinn und Bedeutung") and "The Thought" ("Der Gedanke") are widely cited. Read more...- Analytical feminism is a line of philosophy that applies analytic concepts and methods to feminist issues and applies feminist concepts and insights to issues that have traditionally been of interest to analytic philosophers. Like all feminists, analytical feminists insist on recognizing and contesting sexism and androcentrism. Read more...
Need help?
Do you have a question about Analytic philosophy that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Analytic philosophy-related articles, see WikiProject Analytic philosophy.
Selected images
Subcategories
- Select [►] to view subcategories
Subtopics
| Related articles |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theories | |||||||||||||||
| Concepts |
| ||||||||||||||
| Philosophers |
| ||||||||||||||
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikibooks
Books
Commons
Media
Wikinews
News
Wikiquote
Quotations
Wikisource
Texts
Wikiversity
Learning resources
Wiktionary
Definitions
Wikidata
Database
- What are portals?
- List of portals












_(cropped).jpg/220px-Peter_Singer_no_Fronteiras_do_Pensamento_Porto_Alegre_(9619604688)_(cropped).jpg)