Pain
| Pain | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A woman grimacing while having blood drawn | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain's widely used definition defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage";[1] however, due to it being a complex, subjective phenomenon, defining pain has been a challenge. In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition.
Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future.[2] Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease.[3]
Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries.[4][5] It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning.[6] Simple pain medications are useful in 20% to 70% of cases.[7] Psychological factors such as social support, hypnotic suggestion, excitement, or distraction can significantly affect pain's intensity or unpleasantness.[8][9] In some debates regarding physician-assisted suicide or euthanasia, pain has been used as an argument to permit people who are terminally ill to end their lives.[10]
Classification[edit]
Duration[edit]
Pain is usually transitory, lasting only until the noxious stimulus is removed or the underlying damage or pathology has healed, but some painful conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, peripheral neuropathy, cancer and idiopathic pain, may persist for years. Pain that lasts a long time is called chronic or persistent, and pain that resolves quickly is called acute. Traditionally, the distinction between acute and chronic pain has relied upon an arbitrary interval of time from onset; the two most commonly used markers being 3 months and 6 months since the onset of pain,[11] though some theorists and researchers have placed the transition from acute to chronic pain at 12 months.[12]:93 Others apply acute to pain that lasts less than 30 days, chronic to pain of more than six months' duration, and subacute to pain that lasts from one to six months.[13] A popular alternative definition of chronic pain, involving no arbitrarily fixed durations, is "pain that extends beyond the expected period of healing".[11] Chronic pain may be classified as cancer pain or else as benign.[13]
Nociceptive[edit]
Nociceptive pain is caused by stimulation of sensory nerve fibers that respond to stimuli approaching or exceeding harmful intensity (nociceptors), and may be classified according to the mode of noxious stimulation. The most common categories are "thermal" (e.g. heat or cold), "mechanical" (e.g. crushing, tearing, shearing, etc.) and "chemical" (e.g. iodine in a cut or chemicals released during inflammation). Some nociceptors respond to more than one of these modalities and are consequently designated polymodal.
Nociceptive pain may also be divided into "visceral", "deep somatic" and "superficial somatic" pain. Visceral structures are highly sensitive to stretch, ischemia and inflammation, but relatively insensitive to other stimuli that normally evoke pain in other structures, such as burning and cutting. Visceral pain is diffuse, difficult to locate and often referred to as distant, usually superficial, structure. It may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting and may be described as sickening, deep, squeezing, and dull.[14] Deep somatic pain is initiated by stimulation of nociceptors in ligaments, tendons, bones, blood vessels, fasciae and muscles, and is dull, aching, poorly-localized pain. Examples include sprains and broken bones. Superficial pain is initiated by activation of nociceptors in the skin or other superficial tissue, and is sharp, well-defined and clearly located. Examples of injuries that produce superficial somatic pain include minor wounds and minor (first degree) burns.[12]
Neuropathic[edit]
Neuropathic pain is caused by damage or disease affecting any part of the nervous system involved in bodily feelings (the somatosensory system).[15] Neuropathic pain may be divided into peripheral, central, or mixed (peripheral and central) neuropathic pain. Peripheral neuropathic pain is often described as "burning", "tingling", "electrical", "stabbing", or "pins and needles".[16] Bumping the "funny bone" elicits acute peripheral neuropathic pain.
Allodynia[edit]
Allodynia is pain experienced in response to a normally painless stimulus.[17] It has no biological function and is classified by stimuli into dynamic mechanical, punctate and static.[17][18] In osteoarthritis, NGF has been identified as being involved in allodynia.[18] The extent and intensity of sensation can be assessed through locating trigger points and the region of sensation, as well as utilising phantom maps.[17]
Phantom[edit]
Phantom pain is pain felt in a part of the body that has been amputated, or from which the brain no longer receives signals. It is a type of neuropathic pain.[19]
The prevalence of phantom pain in upper limb amputees is nearly 82%, and in lower limb amputees is 54%.[19] One study found that eight days after amputation, 72% of patients had phantom limb pain, and six months later, 67% reported it.[20][21] Some amputees experience continuous pain that varies in intensity or quality; others experience several bouts of pain per day, or it may reoccur less often. It is often described as shooting, crushing, burning or cramping. If the pain is continuous for a long period, parts of the intact body may become sensitized, so that touching them evokes pain in the phantom limb. Phantom limb pain may accompany urination or defecation.[22]:61–9
Local anesthetic injections into the nerves or sensitive areas of the stump may relieve pain for days, weeks, or sometimes permanently, despite the drug wearing off in a matter of hours; and small injections of hypertonic saline into the soft tissue between vertebrae produces local pain that radiates into the phantom limb for ten minutes or so and may be followed by hours, weeks or even longer of partial or total relief from phantom pain. Vigorous vibration or electrical stimulation of the stump, or current from electrodes surgically implanted onto the spinal cord, all produce relief in some patients.[22]:61–9
Mirror box therapy produces the illusion of movement and touch in a phantom limb which in turn may cause a reduction in pain.[23]
Paraplegia, the loss of sensation and voluntary motor control after serious spinal cord damage, may be accompanied by girdle pain at the level of the spinal cord damage, visceral pain evoked by a filling bladder or bowel, or, in five to ten per cent of paraplegics, phantom body pain in areas of complete sensory loss. This phantom body pain is initially described as burning or tingling, but may evolve into severe crushing or pinching pain, or the sensation of fire running down the legs or of a knife twisting in the flesh. Onset may be immediate or may not occur until years after the disabling injury. Surgical treatment rarely provides lasting relief.[22]:61–9
Psychogenic[edit]
Psychogenic pain, also called psychalgia or somatoform pain, is pain caused, increased, or prolonged by mental, emotional, or behavioral factors.[24] Headache, back pain, and stomach pain are sometimes diagnosed as psychogenic.[24] Sufferers are often stigmatized, because both medical professionals and the general public tend to think that pain from a psychological source is not "real". However, specialists consider that it is no less actual or hurtful than pain from any other source.[25]
People with long-term pain frequently display psychological disturbance, with elevated scores on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory scales of hysteria, depression and hypochondriasis (the "neurotic triad"). Some investigators have argued that it is this neuroticism that causes acute pain to turn chronic, but clinical evidence points the other direction, to chronic pain causing neuroticism. When long-term pain is relieved by therapeutic intervention, scores on the neurotic triad and anxiety fall, often to normal levels. Self-esteem, often low in chronic pain patients, also shows improvement once pain has resolved.[22]:31–2
Breakthrough pain[edit]
Breakthrough pain is transitory pain that comes on suddenly and is not alleviated by the patient's regular pain management. It is common in cancer patients who often have background pain that is generally well-controlled by medications, but who also sometimes experience bouts of severe pain that from time to time "breaks through" the medication. The characteristics of breakthrough cancer pain vary from person to person and according to the cause. Management of breakthrough pain can entail intensive use of opioids, including fentanyl.[26][27][28]
Pain asymbolia and insensitivity[edit]
The ability to experience pain is essential for protection from injury, and recognition of the presence of injury. Episodic analgesia may occur under special circumstances, such as in the excitement of sport or war: a soldier on the battlefield may feel no pain for many hours from a traumatic amputation or other severe injury.[29]
Although unpleasantness is an essential part of the IASP definition of pain,[1] it is possible to induce a state described as intense pain devoid of unpleasantness in some patients, with morphine injection or psychosurgery.[25] Such patients report that they have pain but are not bothered by it; they recognize the sensation of pain but suffer little, or not at all.[30] Indifference to pain can also rarely be present from birth; these people have normal nerves on medical investigations, and find pain unpleasant, but do not avoid repetition of the pain stimulus.[31]
Insensitivity to pain may also result from abnormalities in the nervous system. This is usually the result of acquired damage to the nerves, such as spinal cord injury, diabetes mellitus (diabetic neuropathy), or leprosy in countries where that disease is prevalent.[32] These individuals are at risk of tissue damage and infection due to undiscovered injuries. People with diabetes-related nerve damage, for instance, sustain poorly-healing foot ulcers as a result of decreased sensation.[33]
A much smaller number of people are insensitive to pain due to an inborn abnormality of the nervous system, known as "congenital insensitivity to pain".[31] Children with this condition incur carelessly-repeated damage to their tongues, eyes, joints, skin, and muscles. Some die before adulthood, and others have a reduced life expectancy.[citation needed] Most people with congenital insensitivity to pain have one of five hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies (which includes familial dysautonomia and congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis).[34] These conditions feature decreased sensitivity to pain together with other neurological abnormalities, particularly of the autonomic nervous system.[31][34] A very rare syndrome with isolated congenital insensitivity to pain has been linked with mutations in the SCN9A gene, which codes for a sodium channel (Nav1.7) necessary in conducting pain nerve stimuli.[35]
Effects of acute pain[edit]
Effects on functioning[edit]
Experimental subjects challenged by acute pain and patients in chronic pain experience impairments in attention control, working memory, mental flexibility, problem solving, and information processing speed.[36] Acute and chronic pain are also associated with increased depression, anxiety, fear, and anger.[37]
If I have matters right, the consequences of pain will include direct physical distress, unemployment, financial difficulties, marital disharmony, and difficulties in concentration and attention…
— Harold Merskey 2000[38]
Effects on subsequent negative emotional affect[edit]
Although pain is considered to be aversive and unpleasant and is therefore usually avoided, a meta-analysis which summarized and evaluated numerous studies from various psychological disciplines, found a reduction in negative affect. Across studies, participants that were subjected to acute physical pain in the laboratory subsequently reported feeling better than those in non-painful control conditions, a finding which was also reflected in physiological parameters.[39] A potential mechanism to explain this effect is provided by the opponent-process theory.
Theory[edit]
Historical theories[edit]
Before the relatively recent discovery of neurons and their role in pain, various different body functions were proposed to account for pain. There were several competing early theories of pain among the ancient Greeks: Hippocrates believed that it was due to an imbalance in vital fluids.[40] In the 11th century, Avicenna theorized that there were a number of feeling senses including touch, pain and titillation.[41]
In 1644, René Descartes theorized that pain was a disturbance that passed down along nerve fibers until the disturbance reached the brain.[40][42] Descartes's work, along with Avicenna's, prefigured the 19th-century development of specificity theory. Specificity theory saw pain as "a specific sensation, with its own sensory apparatus independent of touch and other senses".[43] Another theory that came to prominence in the 18th and 19th centuries was intensive theory, which conceived of pain not as a unique sensory modality, but an emotional state produced by stronger than normal stimuli such as intense light, pressure or temperature.[44] By the mid-1890s, specificity was backed mostly by physiologists and physicians, and the intensive theory was mostly backed by psychologists. However, after a series of clinical observations by Henry Head and experiments by Max von Frey, the psychologists migrated to specificity almost en masse, and by century's end, most textbooks on physiology and psychology were presenting pain specificity as fact.[41][43]
In 1955, DC Sinclair and G Weddell developed peripheral pattern theory, based on a 1934 suggestion by John Paul Nafe. They proposed that all skin fiber endings (with the exception of those innervating hair cells) are identical, and that pain is produced by intense stimulation of these fibers.[43] Another 20th-century theory was gate control theory, introduced by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall in the 1965 Science article "Pain Mechanisms: A New Theory".[45] The authors proposed that both thin (pain) and large diameter (touch, pressure, vibration) nerve fibers carry information from the site of injury to two destinations in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, and that the more large fiber activity relative to thin fiber activity at the inhibitory cell, the less pain is felt.[42]
Three dimensions of pain[edit]
In 1968 Ronald Melzack and Kenneth Casey described chronic pain in terms of its three dimensions:
- "sensory-discriminative" (sense of the intensity, location, quality and duration of the pain),
- "affective-motivational" (unpleasantness and urge to escape the unpleasantness), and
- "cognitive-evaluative" (cognitions such as appraisal, cultural values, distraction and hypnotic suggestion).[9]
They theorized that pain intensity (the sensory discriminative dimension) and unpleasantness (the affective-motivational dimension) are not simply determined by the magnitude of the painful stimulus, but "higher" cognitive activities can influence perceived intensity and unpleasantness. Cognitive activities "may affect both sensory and affective experience or they may modify primarily the affective-motivational dimension. Thus, excitement in games or war appears to block both dimensions of pain, while suggestion and placebos may modulate the affective-motivational dimension and leave the sensory-discriminative dimension relatively undisturbed." (p. 432) The paper ends with a call to action: "Pain can be treated not only by trying to cut down the sensory input by anesthetic block, surgical intervention and the like, but also by influencing the motivational-affective and cognitive factors as well." (p. 435)
Theory today[edit]
Wilhelm Erb's (1874) "intensive" theory, that a pain signal can be generated by intense enough stimulation of any sensory receptor, has been soundly disproved. Some sensory fibers do not differentiate between noxious and non-noxious stimuli, while others, nociceptors, respond only to noxious, high intensity stimuli. At the peripheral end of the nociceptor, noxious stimuli generate currents that, above a given threshold, send signals along the nerve fiber to the spinal cord. The "specificity" (whether it responds to thermal, chemical or mechanical features of its environment) of a nociceptor is determined by which ion channels it expresses at its peripheral end. Dozens of different types of nociceptor ion channels have so far been identified, and their exact functions are still being determined.[46]
The pain signal travels from the periphery to the spinal cord along an A-delta or C fiber. Because the A-delta fiber is thicker than the C fiber, and is thinly sheathed in an electrically insulating material (myelin), it carries its signal faster (5–30 m/s) than the unmyelinated C fiber (0.5–2 m/s).[47] Pain evoked by the A-delta fibers is described as sharp and is felt first. This is followed by a duller pain, often described as burning, carried by the C fibers.[48] These "first order" neurons enter the spinal cord via Lissauer's tract.
These A-delta and C fibers connect with "second order" nerve fibers in the central gelatinous substance of the spinal cord (laminae II and III of the dorsal horns). The second order fibers then cross the cord via the anterior white commissure and ascend in the spinothalamic tract. Before reaching the brain, the spinothalamic tract splits into the lateral, neospinothalamic tract and the medial, paleospinothalamic tract.[49]
Second order, spinal cord fibers dedicated to carrying A-delta fiber pain signals, and others that carry both A-delta and C fiber pain signals to the thalamus have been identified. Other spinal cord fibers, known as wide dynamic range neurons, respond to A-delta and C fibers, but also to the large A-beta fibers that carry touch, pressure and vibration signals.[47] Pain-related activity in the thalamus spreads to the insular cortex (thought to embody, among other things, the feeling that distinguishes pain from other homeostatic emotions such as itch and nausea) and anterior cingulate cortex (thought to embody, among other things, the affective/motivational element, the unpleasantness of pain).[50] Pain that is distinctly located also activates primary and secondary somatosensory cortex.[51]
Evolutionary and behavioral role[edit]
Pain is part of the body's defense system, producing a reflexive retraction from the painful stimulus, and tendencies to protect the affected body part while it heals, and avoid that harmful situation in the future.[2][52] It is an important part of animal life, vital to healthy survival. People with congenital insensitivity to pain have reduced life expectancy.[31]
In The Greatest Show on Earth: The Evidence for Evolution, biologist Richard Dawkins addresses the question of why pain should have the quality of being painful. He describes the alternative as a mental raising of a "red flag". To argue why that red flag might be insufficient, Dawkins argues that drives must compete with one other within living beings. The most "fit" creature would be the one whose pains are well balanced. Those pains which mean certain death when ignored will become the most powerfully felt. The relative intensities of pain, then, may resemble the relative importance of that risk to our ancestors.[a] This resemblance will not be perfect, however, because natural selection can be a poor designer. This may have maladaptive results such as supernormal stimuli.[53]
Idiopathic pain (pain that persists after the trauma or pathology has healed, or that arises without any apparent cause) may be an exception to the idea that pain is helpful to survival, although some psychodynamic psychologists argue that such pain is psychogenic, enlisted as a protective distraction to keep dangerous emotions unconscious.[54]
Thresholds[edit]
In pain science, thresholds are measured by gradually increasing the intensity of a stimulus such as electric current or heat applied to the body. The pain perception threshold is the point at which the stimulus begins to hurt, and the pain tolerance threshold is reached when the subject acts to stop the pain.
Differences in pain perception and tolerance thresholds are associated with, among other factors, ethnicity, genetics, and gender. People of Mediterranean origin report as painful some radiant heat intensities that northern Europeans describe as nonpainful. And Italian women tolerate a lesser level of intense electric shock than Jewish or Native American women. Some individuals in all cultures have significantly higher than normal pain perception and tolerance thresholds. For instance, patients who experience painless heart attacks have higher pain thresholds for electric shock, muscle cramp and heat.[22]:17–9
Assessment[edit]
A person's self-report is the most reliable measure of pain.[55][56][57] Some health care professionals may underestimate pain severity.[58] A definition of pain widely employed in nursing, emphasizing its subjective nature and the importance of believing patient reports, was introduced by Margo McCaffery in 1968: "Pain is whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever he says it does".[59] To assess intensity, the patient may be asked to locate their pain on a scale of 0 to 10, with 0 being no pain at all, and 10 the worst pain they have ever felt. Quality can be established by having the patient complete the McGill Pain Questionnaire indicating which words best describe their pain.[6]
Visual analogue scale[edit]
The visual analogue scale is a common, reproducible tool in the assessment of pain and pain relief.[60] The scale is a continuous line anchored by verbal descriptors, one for each extreme of pain where a higher score indicates greater pain intensity. It is usually 10 cm in length with no intermediate descriptors as to avoid marking of scores around a preferred numeric value. When applied as a pain descriptor, these anchors are often 'no pain' and 'worst imaginable pain". Cut-offs for pain classification have been recommended as no pain (0-4mm), mild pain (5-44mm), moderate pain (45-74mm) and severe pain (75-100mm).[61]
Multidimensional pain inventory[edit]
The Multidimensional Pain Inventory (MPI) is a questionnaire designed to assess the psychosocial state of a person with chronic pain. Analysis of MPI results by Turk and Rudy (1988) found three classes of chronic pain patient: "(a) dysfunctional, people who perceived the severity of their pain to be high, reported that pain interfered with much of their lives, reported a higher degree of psychological distress caused by pain, and reported low levels of activity; (b) interpersonally distressed, people with a common perception that significant others were not very supportive of their pain problems; and (c) adaptive copers, patients who reported high levels of social support, relatively low levels of pain and perceived interference, and relatively high levels of activity."[62] Combining the MPI characterization of the person with their IASP five-category pain profile is recommended for deriving the most useful case description.[11]
Assessment in people who are non-verbal[edit]
When a person is non-verbal and cannot self-report pain, observation becomes critical, and specific behaviors can be monitored as pain indicators. Behaviors such as facial grimacing and guarding indicate pain, as well as an increase or decrease in vocalizations, changes in routine behavior patterns and mental status changes. Patients experiencing pain may exhibit withdrawn social behavior and possibly experience a decreased appetite and decreased nutritional intake. A change in condition that deviates from baseline such as moaning with movement or when manipulating a body part, and limited range of motion are also potential pain indicators. In patients who possess language but are incapable of expressing themselves effectively, such as those with dementia, an increase in confusion or display of aggressive behaviors or agitation may signal that discomfort exists, and further assessment is necessary.
Infants do feel pain, but lack the language needed to report it, and so communicate distress by crying. A non-verbal pain assessment should be conducted involving the parents, who will notice changes in the infant which may not be obvious to the health care provider. Pre-term babies are more sensitive to painful stimuli than those carried to full term.[63]
Other barriers to reporting[edit]
The way in which one experiences and responds to pain is related to sociocultural characteristics, such as gender, ethnicity, and age.[64][65] An aging adult may not respond to pain in the same way that a younger person might. Their ability to recognize pain may be blunted by illness or the use of medication. Depression may also keep older adult from reporting they are in pain. Decline in self-care may also indicate the older adult is experiencing pain. They may be reluctant to report pain because they do not want to be perceived as weak, or may feel it is impolite or shameful to complain, or they may feel the pain is a form of deserved punishment.[66][67]
Cultural barriers may also affect the likelihood of reporting pain. Sufferers may feel that certain treatments go against their religious beliefs. They may not report pain because they feel it is a sign that death is near. Many people fear the stigma of addiction, and avoid pain treatment so as not to be prescribed potentially addicting drugs. Many Asians do not want to lose respect in society by admitting they are in pain and need help, believing the pain should be borne in silence, while other cultures feel they should report pain immediately to receive immediate relief.[63] Gender can also be a factor in reporting pain. Gender differences can be the result of social and cultural expectations, with women expected to be more emotional and show pain, and men more stoic.[63]
As an aid to diagnosis[edit]
Pain is a symptom of many medical conditions. Knowing the time of onset, location, intensity, pattern of occurrence (continuous, intermittent, etc.), exacerbating and relieving factors, and quality (burning, sharp, etc.) of the pain will help the examining physician to accurately diagnose the problem. For example, chest pain described as extreme heaviness may indicate myocardial infarction, while chest pain described as tearing may indicate aortic dissection.[68][69]
Physiological measurement of pain[edit]
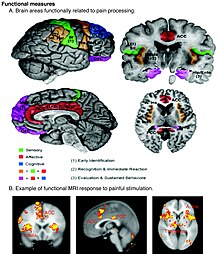
Functional magnetic resonance imaging brain scanning has been used to measure pain, and correlates well with self-reported pain.[70][71][72]
Management[edit]
Inadequate treatment of pain is widespread throughout surgical wards, intensive care units, and accident and emergency departments In general practice, the management of all forms of chronic pain including cancer pain, and in end of life care.[73][74][75][76][77][78][79] This neglect extends to all ages, from newborns to medically frail elderly.[80][81] African and Hispanic Americans are more likely than others to suffer unnecessarily while in the care of a physician;[82][83] and women's pain is more likely to be undertreated than men's.[84]
The International Association for the Study of Pain advocates that the relief of pain should be recognized as a human right, that chronic pain should be considered a disease in its own right, and that pain medicine should have the full status of a medical specialty.[85] It is a specialty only in China and Australia at this time.[86] Elsewhere, pain medicine is a subspecialty under disciplines such as anesthesiology, physiatry, neurology, palliative medicine and psychiatry.[87] In 2011, Human Rights Watch alerted that tens of millions of people worldwide are still denied access to inexpensive medications for severe pain.[88]
Breastfeeding may decrease pain when babies are immunized.[89]
Medication[edit]
Acute pain is usually managed with medications such as analgesics and anesthetics. Caffeine when added to pain medications such as ibuprofen, may provide some additional benefit.[90][91] Ketamine can be used instead of opiods for short term pain.[92] Management of chronic pain, however, is more difficult, and may require the coordinated efforts of a pain management team, which typically includes medical practitioners, clinical pharmacists, clinical psychologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners.[93]
Sugar (sucrose) when taken by mouth reduces pain in newborn babies undergoing some medical procedures (a lancing of the heel, venipuncture, and intramuscular injections). Sugar does not remove pain from circumcision, and it is unknown if sugar reduces pain for other procedures.[94] Sugar did not affect pain-related electrical activity in the brains of newborns one second after the heel lance procedure.[95] Sweet liquid by mouth moderately reduces the rate and duration of crying caused by immunization injection in children between one and twelve months of age.[96]
Psychological[edit]
Individuals with more social support experience less cancer pain, take less pain medication, report less labor pain and are less likely to use epidural anesthesia during childbirth, or suffer from chest pain after coronary artery bypass surgery.[97]
Suggestion can significantly affect pain intensity. About 35% of people report marked relief after receiving a saline injection they believed to be morphine. This placebo effect is more pronounced in people who are prone to anxiety, and so anxiety reduction may account for some of the effect, but it does not account for all of it. Placebos are more effective for intense pain than mild pain; and they produce progressively weaker effects with repeated administration.[22]:26–8 It is possible for many with chronic pain to become so absorbed in an activity or entertainment that the pain is no longer felt, or is greatly diminished.[22]:22–3
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown effective for improving quality of life in those with chronic pain but the reduction in suffering is modest, and the CBT method was not shown to have any effect on outcome.[98] Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) may also effective in the treatment of chronic pain.[99]
A number of meta-analyses have found clinical hypnosis to be effective in controlling pain associated with diagnostic and surgical procedures in both adults and children, as well as pain associated with cancer and childbirth.[100] A 2007 review of 13 studies found evidence for the efficacy of hypnosis in the reduction of chronic pain under some conditions, though the number of patients enrolled in the studies was low, raising issues related to the statistical power to detect group differences, and most lacked credible controls for placebo or expectation. The authors concluded that "although the findings provide support for the general applicability of hypnosis in the treatment of chronic pain, considerably more research will be needed to fully determine the effects of hypnosis for different chronic-pain conditions."[101]
Alternative medicine[edit]
Pain is the most common reason for people to use complementary and alternative medicine.[102] An analysis of the 13 highest quality studies of pain treatment with acupuncture, published in January 2009, concluded there was little difference in the effect of real, faked and no acupuncture.[103] However, other reviews have found some benefit.[104][105][106] Additionally, there is tentative evidence for a few herbal medicines.[107] There has been some interest in the relationship between vitamin D and pain, but the evidence so far from controlled trials for such a relationship, other than in osteomalacia, is inconclusive.[108]
A 2003 meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials found that spinal manipulation was "more effective than sham therapy but was no more or less effective than general practitioner care, analgesics, physical therapy, exercise, or back school" in the treatment of lower back pain.[109]
Epidemiology[edit]
Pain is the main reason for visiting an emergency department in more than 50% of cases,[110] and is present in 30% of family practice visits.[111] Several epidemiological studies have reported widely varying prevalence rates for chronic pain, ranging from 12 to 80% of the population.[112] It becomes more common as people approach death. A study of 4,703 patients found that 26% had pain in the last two years of life, increasing to 46% in the last month.[113]
A survey of 6,636 children (0–18 years of age) found that, of the 5,424 respondents, 54% had experienced pain in the preceding three months. A quarter reported having experienced recurrent or continuous pain for three months or more, and a third of these reported frequent and intense pain. The intensity of chronic pain was higher for girls, and girls' reports of chronic pain increased markedly between ages 12 and 14.[114]
History[edit]
In 1994, responding to the need for a more useful system for describing chronic pain, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) classified pain according to specific characteristics:
- region of the body involved (e.g. abdomen, lower limbs),
- system whose dysfunction may be causing the pain (e.g., nervous, gastrointestinal),
- duration and pattern of occurrence,
- intensity and time since onset, and
- cause[115]
However, this system has been criticized by Clifford J. Woolf and others as inadequate for guiding research and treatment.[116][non-primary source needed] Woolf suggests three classes of pain:
- nociceptive pain,
- inflammatory pain which is associated with tissue damage and the infiltration of immune cells, and
- pathological pain which is a disease state caused by damage to the nervous system or by its abnormal function (e.g. fibromyalgia, peripheral neuropathy, tension type headache, etc.).[117][non-primary source needed]
Society and culture[edit]
The nature or meaning of physical pain has been diversely understood by religious or secular traditions from antiquity to modern times.[118][119]
Physical pain is an important political topic in relation to various issues, including pain management policy, drug control, animal rights or animal welfare, torture, and pain compliance. In various contexts, the deliberate infliction of pain in the form of corporal punishment is used as retribution for an offence, or for the purpose of disciplining or reforming a wrongdoer, or to deter attitudes or behaviour deemed unacceptable. The slow slicing, or death by a thousand cuts, was a form of execution in China reserved for crimes viewed as especially severe, such as high treason or patricide. In some cultures, extreme practices such as mortification of the flesh or painful rites of passage are highly regarded. For example, the Sateré-Mawé people of Brazil use intentional bullet ant stings as part of their initiation rites to become warriors.[120]
Other animals[edit]
The most reliable method for assessing pain in most humans is by asking a question: a person may report pain that cannot be detected by any known physiological measure. However, like infants, animals cannot answer questions about whether they feel pain; thus the defining criterion for pain in humans cannot be applied to them. Philosophers and scientists have responded to this difficulty in a variety of ways. René Descartes for example argued that animals lack consciousness and therefore do not experience pain and suffering in the way that humans do.[121] Bernard Rollin of Colorado State University, the principal author of two U.S. federal laws regulating pain relief for animals,[b] writes that researchers remained unsure into the 1980s as to whether animals experience pain, and that veterinarians trained in the U.S. before 1989 were simply taught to ignore animal pain.[123] In his interactions with scientists and other veterinarians, he was regularly asked to "prove" that animals are conscious, and to provide "scientifically acceptable" grounds for claiming that they feel pain.[123] Carbone writes that the view that animals feel pain differently is now a minority view.[citation needed] Academic reviews of the topic are more equivocal, noting that although the argument that animals have at least simple conscious thoughts and feelings has strong support,[124] some critics continue to question how reliably animal mental states can be determined.[121][125] The ability of invertebrate species of animals, such as insects, to feel pain and suffering is also unclear.[126][127][128]
The presence of pain in an animal cannot be known for certain, but it can be inferred through physical and behavioral reactions.[129] Specialists currently believe that all vertebrates can feel pain, and that certain invertebrates, like the octopus, may also.[126][130][131] As for other animals, plants, or other entities, their ability to feel physical pain is at present a question beyond scientific reach, since no mechanism is known by which they could have such a feeling. In particular, there are no known nociceptors in groups such as plants, fungi, and most insects,[132] except for instance in fruit flies.[133]
In vertebrates, endogenous opioids are neuromodulators that moderate pain by interacting with opioid receptors.[134] Opioids and opioid receptors occur naturally in crustaceans and, although at present no certain conclusion can be drawn,[135] their presence indicates that lobsters may be able to experience pain.[135][136] Opioids may mediate their pain in the same way as in vertebrates.[136] Veterinary medicine uses, for actual or potential animal pain, the same analgesics and anesthetics as used in humans.[137]
Etymology[edit]
First attested in English in 1297, the word peyn comes from the Old French peine, in turn from Latin poena meaning "punishment, penalty"[138] (in L.L. also meaning "torment, hardship, suffering") and that from Greek ποινή (poine), generally meaning "price paid, penalty, punishment".[139][140]
See also[edit]
 Pain portal
Pain portal- Hedonic adaptation, the tendency to quickly return to a relatively stable level of happiness despite major positive or negative events
- Pain and suffering, the legal term for the physical and emotional stress caused from an injury
- Pain (philosophy), the branch of philosophy concerned with suffering and physical pain
Notes[edit]
- ^ For example, lack of food, extreme cold, or serious injuries are felt as exceptionally painful, whereas minor damage is felt as mere discomfort
- ^ Rollin drafted the 1985 Health Research Extension Act and an animal welfare amendment to the 1985 Food Security Act.[122]
References[edit]
- ^ a b "International Association for the Study of Pain: Pain Definitions". Archived from the original on 13 January 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage
Derived from The need of a taxonomy. Pain. 1979;6(3):247–8. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(79)90046-0. PMID 460931. - ^ a b The neurobiology of pain: Symposium of the Northern Neurobiology Group, held at Leeds on 18 April 1983. Manchester: Manchester University Press; 1984. ISBN 9780719009969. Cutaneous nociceptors. p. 106.
- ^ The Handbook of Chronic Pain. Nova Biomedical Books; 2007. ISBN 9781600210440. Taxonomy and classification of pain.
- ^ Debono, DJ; Hoeksema, LJ; Hobbs, RD (August 2013). "Caring for Patients with Chronic Pain: Pearls and Pitfalls". Journal of the American Osteopathic Association. 113 (8): 620–627. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2013.023. PMID 23918913.
- ^ What should be the core outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials?. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 2004;6(4):151–4. doi:10.1186/ar1196. PMID 15225358.
- ^ a b Assessment of pain. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101(1):17–24. doi:10.1093/bja/aen103. PMID 18487245.
- ^ Moore, RA; Wiffen, PJ; Derry, S; Maguire, T; Roy, YM; Tyrrell, L (4 November 2015). "Non-prescription (OTC) oral analgesics for acute pain - an overview of Cochrane reviews". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD010794. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010794.pub2. PMID 26544675.
- ^ The Social Outcast: Ostracism, Social Exclusion, Rejection, & Bullying (Sydney Symposium of Social Psychology). East Sussex: Psychology Press; 2005. ISBN 9781841694245. Why it hurts to be left out: The neurocognitive overlap between physical and social pain. p. 210.
- ^ a b The skin senses: Proceedings of the first International Symposium on the Skin Senses, held at the Florida State University in Tallahassee, Florida. Sensory, motivational and central control determinants of chronic pain: A new conceptual model. p. 432.
- ^ Weyers, H (September 2006). "Explaining the emergence of euthanasia law in the Netherlands: how the sociology of law can help the sociology of bioethics". Sociology of Health & Illness. 28 (6): 802–16. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.2006.00543.x. PMID 17184419.
- ^ a b c Bonica's management of pain. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. ISBN 9780781768276. Pain terms and taxonomies of pain.
- ^ a b Pain management: an interdisciplinary approach. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. ISBN 9780443056833. General considerations of acute pain.
- ^ a b Pain management: a practical guide for clinicians. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2002. ISBN 9780849322624. Classification of pain. p. 28.
- ^ Pathophysiology of somatic, visceral, and neuropathic cancer pain. In: Sykes N, Bennett MI & Yuan C-S. Clinical pain management: Cancer pain. 2 ed. London: Hodder Arnold; ISBN 978-0-340-94007-5. p. 3–12.
- ^ Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008 [archived 20 November 2008];70(18):1630–5. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59. PMID 18003941.
- ^ Mechanisms and management of neuropathic pain in cancer. J. Support Oncol.. 2003 [archived 7 January 2010];1(2):107–20. PMID 15352654.
- ^ a b c Jensen, Troels S; Finnerup, Nanna B (2014). "Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms". The Lancet Neurology. 13 (9): 924–935. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(14)70102-4. PMID 25142459.
- ^ a b Lolignier, Stéphane; Eijkelkamp, Niels; Wood, John N. (2015-01-01). "Mechanical allodynia". Pflügers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 467 (1): 133–139. doi:10.1007/s00424-014-1532-0. ISSN 0031-6768. PMC 4281368. PMID 24846747.
- ^ a b Phantom pain and phantom sensations in upper limb amputees: an epidemiological study. Pain. 2000;87(1):33–41. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00264-5. PMID 10863043.
- ^ Phantom limb, phantom pain and stump pain in amputees during the first 6 months following limb amputation. Pain. 1983;17(3):243–56. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(83)90097-0. PMID 6657285.
- ^ Immediate and long-term phantom limb pain in amputees: incidence, clinical characteristics and relationship to pre-amputation limb pain. Pain. 1985;21(3):267–78. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(85)90090-9. PMID 3991231.
- ^ a b c d e f g The challenge of pain. 2nd ed. New York: Penguin Books; 1996. ISBN 9780140256703.
- ^ Synaesthesia in phantom limbs induced with mirrors. Proc. Biol. Sci.. 1996;263(1369):377–86. doi:10.1098/rspb.1996.0058. PMID 8637922.
- ^ a b "Psychogenic Pain". Cleveland Clinic. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- ^ a b "International Association for the Study of Pain | Pain Definitions".. Retrieved 12 October 2010.
- ^ Mishra, S; Bhatnagar, S; Chaudhary, P; Rana, SP (January 2009). "Breakthrough cancer pain: review of prevalence, characteristics and management". Indian Journal of Palliative Care. 15 (1): 14–8. doi:10.4103/0973-1075.53506. PMC 2886208. PMID 20606850. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014.
- ^ Caraceni, A; Hanks, G; Kaasa, S; Bennett, MI; Brunelli, C; Cherny, N; Dale, O; De Conno, F; Fallon, M; Hanna, M; Haugen, DF; Juhl, G; King, S; Klepstad, P; Laugsand, EA; Maltonib, M; Mercadante, S; Nabal, M; Pigni, A; Radbruch, L; Reid, C; Sjogren, P; Stone, PC; Tassinari, D; Zeppetella, G (February 2012). "Use of opioid analgesics in the treatment of cancer pain: evidence-based recommendations from the EAPC" (PDF). The Lancet Oncology. 13 (2): e58–68. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70040-2. PMID 22300860. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2014.
- ^ Zeppetella, G; Davies, AN (2013). "Opioids for the management of breakthrough pain in cancer patients". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (10): CD004311. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004311.pub3. PMID 24142465.
- ^ Beecher, HK (1959). Measurement of subjective responses. New York: Oxford University Press. cited in Melzack, R; Wall, PD (1996). The challenge of pain (2 ed.). London: Penguin. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-14-025670-3.
- ^ Nikola Grahek, Feeling pain and being in pain Archived 27 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Oldenburg, 2001. ISBN 9780262517324.
- ^ a b c d Congenital insensitivity to pain: an update. Pain. 2003;101(3):213–9. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00482-7. PMID 12583863.
- ^ The gift of pain: why we hurt & what we can do about it. Grand Rapids, Mich: Zondervan Publ; 1997. ISBN 9780310221449.
- ^ Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis.. 2004;39(7):885–910. doi:10.1086/424846. PMID 15472838.
- ^ a b Inherited autonomic neuropathies. Semin Neurol. 2003;23(4):381–90. doi:10.1055/s-2004-817722. PMID 15088259.
- ^ Pain as a channelopathy. J. Clin. Invest.. 2010;120(11):3745–52. doi:10.1172/JCI43158. PMID 21041956.
- ^ Cognitive impairment in patients with chronic pain: the significance of stress. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2003;7(2):116–26. doi:10.1007/s11916-003-0021-5. PMID 12628053.
- ^ Pain-related effects of trait anger expression: neural substrates and the role of endogenous opioid mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2009;33(3):475–91. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.12.003. PMID 19146872.
- ^ Personality Characteristics of Patients With Pain. American Psychological Association (APA); 2000. ISBN 1-55798-646-0. The History of Psychoanalitic Ideas Concerning Pain.
- ^ Bresin, K., Kling, L., & Verona, E. (2018): The effect of acute physical pain on subsequent negative emotional affect: A meta-analysis. Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment, 9(3), 273-283 PMID 28368146, doi:10.1037/per0000248
- ^ a b Linton. Models of Pain Perception. Elsevier Health, 2005. Print.
- ^ a b Pain: History and present status. American Journal of Psychology. July 1939;52:331–347. doi:10.2307/1416740.
- ^ a b Pain: psychological perspectives. Mahwah, N.J: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers; 2004. ISBN 9780415650618. The Gate Control Theory: Reaching for the Brain.
- ^ a b c The management of pain. 2 ed. Vol. 1. London: Lea & Febiger; 1990. ISBN 9780812111224. History of pain concepts and therapies. p. 7.
- ^ Origins of neuroscience: a history of explorations into brain function. USA: Oxford University Press; 2001. ISBN 9780195146943.
- ^ Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science. 1965 [archived 14 January 2012];150(3699):971–9. doi:10.1126/science.150.3699.971. PMID 5320816.
- ^ Woolf, CJ; Ma, Q (August 2007). "Nociceptors--noxious stimulus detectors". Neuron. 55 (3): 353–64. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.016. PMID 17678850.
- ^ a b Pharmacology of pain. Seattle: International Association for the Study of Pain Press; 2010. ISBN 978-0-931092-78-7. Applied pain neurophysiology. p. 3–26.
- ^ Psychology of pain. New York: Wiley; 1995. ISBN 9780471957737. p. 9.
- ^ Skevington, S. M. (1995). Psychology of pain. Chichester, UK: Wiley. p. 18. ISBN 9780471957737.
- ^ Pain mechanisms: labeled lines versus convergence in central processing. Annu. Rev. Neurosci.. 2003;26:1–30. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131022. PMID 12651967.
- ^ The functional anatomy of neuropathic pain. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am.. 2004;15(3):257–68. doi:10.1016/j.nec.2004.02.010. PMID 15246335.
- ^ Handbook of Motivation Science. New York: The Guilford Press; 2007. ISBN 9781593855680. The neuroevolution of motivation. p. 191.
- ^ The Greatest Show on Earth. Free Press; 2009.
- ^ The divided mind: the epidemic of mindbody disorders. New York: ReganBooks; 2006. ISBN 9780061174308.
- ^ Amico, Donita (2016). Health & physical assessment in nursing. Boston: Pearson. p. 173. ISBN 9780133876406.
- ^ Taylor, Carol (2015). Fundamentals of nursing : the art and science of person-centered nursing care. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health. p. 241. ISBN 9781451185614.
- ^ Venes, Donald (2013). Taber's cyclopedic medical dictionary. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis. p. 1716. ISBN 9780803629776.
- ^ Underestimation of pain by health-care providers: towards a model of the process of inferring pain in others. Can. J. Nurs. Res.. 2007;39(2):88–106. PMID 17679587.
- ^ McCaffery M. (1968). Nursing practice theories related to cognition, bodily pain, and man-environment interactions. Los Angeles: UCLA Students Store.
More recently, McCaffery defined pain as "whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever the experiencing person says it does." Pain: clinical manual. St. Louis: Mosby; 1999. ISBN 9780815156093. - ^ Kelly, A.-M. (1 May 2001). "The minimum clinically significant difference in visual analogue scale pain score does not differ with severity of pain". Emergency Medicine Journal. 18 (3): 205–207. doi:10.1136/emj.18.3.205. ISSN 1472-0205. PMC 1725574. PMID 11354213. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018.
- ^ Hawker, Gillian A.; Mian, Samra; Kendzerska, Tetyana; French, Melissa (2011-11-01). "Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP)". Arthritis Care & Research. 63 (S11): S240–S252. doi:10.1002/acr.20543. ISSN 2151-4658. PMID 22588748.
- ^ Toward an empirically derived taxonomy of chronic pain patients: integration of psychological assessment data. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol.. 1988;56(2):233–8. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.56.2.233. PMID 3372831.
- ^ a b c Physical examination & health assessment. St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders; 2007. ISBN 9781455728107. p. 180–192.
- ^ Social science and the study of pain since Zborowski: A need for a new agenda. Soc Sci Med. 1993;36(6):783–91. doi:10.1016/0277-9536(93)90039-7.
- ^ Zborowski M. People in Pain. 1969, San Francisco, CA:Josey-Bass
- ^ Social Construction of pain and aging: Individual artfulness within interpretive structures. Symb Interaction. 1997;20(3):251–273. doi:10.1525/si.1997.20.3.251.
- ^ lawhorne, L; Passerini, J (1999). Chronic Pain Management in the Long Term Care Setting: Clinical Practice Guidelines. Baltimore, Maryland: American Medical Directors Association. pp. 1–27.
- ^ The rational clinical examination. Is this patient having a myocardial infarction?. JAMA. 1998;280(14):1256–63. doi:10.1001/jama.280.14.1256. PMID 9786377.
- ^ The clinical recognition of dissecting aortic aneurysm. Am. J. Med.. 1976;60(5):625–33. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(76)90496-4. PMID 1020750.
- ^ Brown. Towards a Physiology-Based Measure of Pain: Patterns of Human Brain Activity Distinguish Painful from Non-Painful Thermal Stimulation. PLOS ONE. September 2011. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024124. PMID 21931652.
- ^ Paddock, Catharine (15 September 2011). "Tool That Measures Pain Objectively Under Way". Medical News Today. Archived from the original on 25 September 2017. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- ^ Reuters Editorial (13 September 2011). "Feeling pain? The computer can tell". Reuters. Archived from the original on 17 June 2015. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- ^ Strategies for postoperative pain management. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2004;18(4):703–17. doi:10.1016/j.bpa.2004.05.004. PMID 15460554.
- ^ Pain management in the culture of critical care. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. North Am.. 2001;13(2):151–66. PMID 11866399.
- ^ Inadequate analgesia in emergency medicine. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2004;43(4):494–503. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2003.11.019. PMID 15039693.
- ^ Primary care of the patient with cancer. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75(8):1207–14. PMID 17477104.
- ^ Evolving role of the neurologist in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic noncancer pain. Mayo Clin. Proc.. 2003;78(1):80–4. doi:10.4065/78.1.80. PMID 12528880.
- ^ Prevalence of undertreatment in cancer pain. A review of published literature. Annals of Oncology. 2008;19(12):1985–91. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn419. PMID 18632721.
- ^ Assessment and management of pain in palliative care patients. Cancer Control. 2001 [archived 12 July 2008];8(1):15–24. PMID 11176032.
- ^ Textbook of pediatric emergency medicine. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. ISBN 9781605471594. Sedation and analgesia.
- ^ Undertreatment of cancer pain in elderly patients. JAMA. 1998;279(23):1914–5. doi:10.1001/jama.279.23.1914. PMID 9634265.
- ^ Race, ethnicity, and pain treatment: striving to understand the causes and solutions to the disparities in pain treatment. J Law Med Ethics. 2001 [archived 19 July 2011];29(1):52–68. PMID 11521272.
- ^ The unequal burden of pain: confronting racial and ethnic disparities in pain. Pain Med. 2003;4(3):277–94. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4637.2003.03034.x. PMID 12974827.
- ^ The girl who cried pain: a bias against women in the treatment of pain. J Law Med Ethics. 2001;29(1):13–27. PMID 11521267.
- ^ Delegates to the International Pain Summit of the International Association for the Study of Pain (2010) "Declaration of Montreal" Archived 13 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Cousins and Bridenbaugh's Neural Blockade in Clinical Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008. ISBN 9780781773881.
- ^ "Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation" Archived 16 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Human Rights Watch (2011). "Tens of Millions Face Death in Agony". Archived from the original on 1 September 2013. Retrieved 26 August 2013.
- ^ Harrison, D; Reszel, J; Bueno, M; Sampson, M; Shah, VS; Taddio, A; Larocque, C; Turner, L (28 October 2016). "Breastfeeding for procedural pain in infants beyond the neonatal period". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10: CD011248. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011248.pub2. PMID 27792244.
- ^ Derry, CJ; Derry, S; Moore, RA (11 December 2014). "Caffeine as an analgesic adjuvant for acute pain in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD009281. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009281.pub3. PMID 25502052.
- ^ Derry, Sheena; Wiffen, Philip J.; Moore, R. Andrew (2015-07-14). "Single dose oral ibuprofen plus caffeine for acute postoperative pain in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD011509. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011509.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 26171993.
- ^ Karlow, N; Schlaepfer, CH; Stoll, CRT; Doering, M; Carpenter, CR; Colditz, GA; Motov, S; Miller, J; Schwarz, ES (17 July 2018). "A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Ketamine as an Alternative to Opioids for Acute Pain in the Emergency Department". Academic Emergency Medicine. 25 (10): 1086–1097. doi:10.1111/acem.13502. PMID 30019434.
- ^ Thienhaus, O; Cole, BE (2002). "The classification of pain". In Weiner, RS. Pain management: A practical guide for clinicians. American Academy of Pain Management. p. 29. ISBN 9780849322624.
- Main, Chris J.; Spanswick, Chris C. (2000). Pain management: an interdisciplinary approach Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 9780443056833.
- ^ Stevens, Bonnie; Yamada, Janet; Ohlsson, Arne; Haliburton, Sarah; Shorkey, Allyson; Yamada, Janet (2016). "Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7: CD001069. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001069.pub5. PMID 27420164.
- ^ Lasky, RE; van Drongelen, W (9 October 2010). "Is sucrose an effective analgesic for newborn babies?". Lancet. 376 (9748): 1201–3. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61358-X. PMID 20817245.
- ^ (June 2010). "Efficacy of sweet solutions for analgesia in infants between 1 and 12 months of age: a systematic review". Arch. Dis. Child.. 95(6):406–13. doi:10.1136/adc.2009.174227. PMID 20463370.
- ^ Eisenberger, NI; Lieberman (2005). "Why it hurts to be left out: The neurocognitive overlap between physical and social pain" Archived 29 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine In Williams, KD; Forgas, JP; von Hippel, W. The social outcast: Ostracism, social exclusion, rejection, and bullying. New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 109–127. ISBN 9781841694245.
- ^ Cognitive-behavioral treatments for chronic pain: what works for whom?. 2005;21(1):1–8. doi:10.1097/00002508-200501000-00001. PMID 15599126.
- ^ Ost, LG (October 2014). "The efficacy of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis". Behaviour Research and Therapy. 61: 105–21. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2014.07.018. PMID 25193001.
- ^ Wark, D.M. (2008). What can we do with hypnosis: A brief note. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00029157.2008.10401640#.UgGMqZLVArU
- ^ Hypnotherapy for the management of chronic pain. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis. 2007;55(3):283. doi:10.1080/00207140701338621. PMID 17558718.
- ^ Why patients use alternative medicine: Results of a national study. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1998;279(19):1548–1553. doi:10.1001/jama.279.19.1548. PMID 9605899.
- ^ Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups. BMJ. 2009;338:a3115. doi:10.1136/bmj.a3115. PMID 19174438.
- ^ Chiu, HY; Hsieh, YJ; Tsai, PS (Feb 7, 2016). "Systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture to reduce cancer-related pain". Eur J Cancer Care. 26 (2): e12457. doi:10.1111/ecc.12457. PMID 26853524.
- ^ Chang, S-C; Hsu, C-H; Hsu, C-K; Yang, SS-D; Chang, S-J (2016). "The efficacy of acupuncture in managing patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A systemic review and meta-analysis". Neurourol Urodyn. 36 (2): 474–481. doi:10.1002/nau.22958. PMID 26741647.
- ^ Ji, M; Wang, X; Chen, M; Shen, Y; Zhang, X; Yang, J (2015). "The Efficacy of Acupuncture for the Treatment of Sciatica: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015: 1–12. doi:10.1155/2015/192808. PMC 4575738. PMID 26425130.
- ^ Gagnier, JJ; Oltean, H; van Tulder, MW; Berman, BM; Bombardier, C; Robbins, CB (2016). "Herbal Medicine for Low Back Pain: A Cochrane Review". Spine. 41 (2): 116–33. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001310. PMID 26630428.
- ^ Vitamin D and chronic pain. Pain. 2009;141(1):10–13. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2008.11.010. PMID 19084336.
- ^ Spinal manipulative therapy for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD000447. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000447.pub2. PMID 14973958.
- ^ The high prevalence of pain in emergency medical care. American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2002;20(3):165–9. doi:10.1053/ajem.2002.32643. PMID 11992334.
- ^ Prevalence of pain in general practice. Eur J Pain. 2002;6(5):375–85. doi:10.1016/S1090-3801(02)00025-3. PMID 12160512.
- ^ Chronic pain: a review. J Med Liban. 2010;58(1):21–7. PMID 20358856.
- ^ The epidemiology of pain during the last 2 years of life. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2010;153(9):563–9. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-153-9-201011020-00005. PMID 21041575.
- ^ Pain in children and adolescents: a common experience. Pain. 2000;87(1):51–8. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00269-4. PMID 10863045.
- ^ Classification of Chronic Pain. 2 ed. Seattle: International Association for the Study of Pain; 1994. ISBN 978-0931092053. p. 3 & 4.
- ^ Towards a mechanism-based classification of pain?. Pain. 1998;77(3):227–9. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(98)00099-2. PMID 9808347.
- ^ What is this thing called pain?. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2010;120(11):3742–4. doi:10.1172/JCI45178. PMID 21041955.
- ^ The history of pain. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1995. ISBN 9780674399686.
- ^ The culture of pain. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1991. ISBN 9780520082762.
- ^ Backshall, Steve (6 January 2008). "Bitten by the Amazon". London: The Sunday Times. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
- ^ a b Working party of the Nuffield Council on Bioethics (2005). "The ethics of research involving animals. London: Nuffield Council on Bioethics." ISBN 9781904384106. Archived from the original on 25 June 2008. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- ^ Animal research: a moral science. Talking Point on the use of animals in scientific research. EMBO Reports. 2007;8(6):521–5. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400996. PMID 17545990.
- ^ a b Rollin, B. (1989) The Unheeded Cry: Animal Consciousness, Animal Pain, and Science. New York: Oxford University Press, pp. xii, 117–118, cited in Carbone 2004, p. 150.
- ^ New evidence of animal consciousness. Anim Cogn. 2004;7(1):5–18. doi:10.1007/s10071-003-0203-x. PMID 14658059.
- ^ Assessing animal cognition: ethological and philosophical perspectives. J. Anim. Sci.. 1998;76(1):42–7. PMID 9464883.
- ^ a b Sherwin, C.M., (2001). Can invertebrates suffer? Or, how robust is argument-by-analogy? Animal Welfare, 10 (supplement): S103-S118
- ^ The Moral Standing of Insects and the Ethics of Extinction. The Florida Entomologist. 1987;70(1):70–89. doi:10.2307/3495093.
- ^ Pain, suffering, and anxiety in animals and humans. Theoretical Medicine and Bioethics. 1991;12(3):193–211. doi:10.1007/BF00489606. PMID 1754965.
- ^ The formalin test: scoring properties of the first and second phases of the pain response in rats. Pain. 1995;60(1):91–102. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(94)00095-V. PMID 7715946.
- ^ "Do Invertebrates Feel Pain?" Archived 6 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine, The Senate Standing Committee on Legal and Constitutional Affairs, The Parliament of Canada Web Site. Retrieved 11 June 2008.
- ^ A Question of Pain in Invertebrates. Institute for laboratory animal research journal. 1991 [archived 8 October 2011];33:1–2.
- ^ Do insects feel pain? A biological view. Experientia. 1984;40:164–167. doi:10.1007/BF01963580.
- ^ painless, a Drosophila gene essential for nociception. Cell. 2003 [archived 29 October 2005];113(2):261–73. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00272-1. PMID 12705873.
- ^ Sukhdeo, M. V. K. (1994-01-01). Parasites and Behaviour. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521485425.
- ^ a b L. Sømme (2005). "Sentience and pain in invertebrates: Report to Norwegian Scientific Committee for Food Safety". Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Oslo.
- ^ a b Cephalopods and decapod crustaceans: their capacity to experience pain and suffering. Advocates for Animals; 2005.
- ^ Pain mechanisms and their implication for the management of pain in farm and companion animals. Vet. J.. 2007;174(2):227–39. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.02.002. PMID 17553712.
- ^ poena Archived 13 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Charlton T. Lewis, Charles Short, A Latin Dictionary, on Perseus Digital Library
- ^ ποινή Archived 13 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus Digital Library
- ^ pain Archived 28 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Online Etymology Dictionary
External links[edit]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pain. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Pain |