Austronesian languages
| Austronesian | |
|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Austronesian peoples |
| Geographic distribution | Maritime and parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Oceania, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Andaman archipelago and parts of Hainan and Madagascar |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Austronesian |
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | map |
| Glottolog | aust1307[1] |
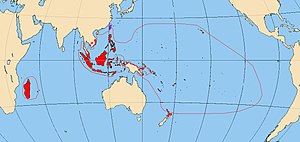 Distribution of Austronesian languages | |
The Austronesian languages are a language family that is widely dispersed throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, Madagascar and the islands of the Pacific Ocean, with a few members in continental Asia.[2] Austronesian languages are spoken by about 386 million people (4.9%), making it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages with the highest number of speakers are Malay (Indonesian and Malaysian), Javanese, and Filipino (Tagalog). The family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family.[3]
Similarities between the languages spoken in the Malay Archipelago and the Pacific Ocean were first observed in 1706 by the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland.[4] In the 19th century, researchers (e.g. Wilhelm von Humboldt, Herman van der Tuuk) started to apply the comparative method to the Austronesian languages, but the first comprehensive and extensive study on the phonological history of the Austronesian language family including a reconstruction of Proto-Austronesian lexicon was made by the German linguist Otto Dempwolff.[5] The term Austronesian itself was coined by Wilhelm Schmidt (German austronesisch, based on Latin auster "south wind" and Greek νῆσος "island").[6] The family is aptly named, as the vast majority of Austronesian languages are spoken on islands: only a few languages, such as Malay and the Chamic languages, are indigenous to mainland Asia. Many Austronesian languages have very few speakers, but the major Austronesian languages are spoken by tens of millions of people and one Austronesian language, Malay (including both Indonesian and Malaysian variants), is spoken by 250 million people, making it the 8th most spoken language in the world. Approximately twenty Austronesian languages are official in their respective countries (see the list of major and official Austronesian languages).
Different sources count languages differently, but Austronesian and Niger–Congo are the two largest language families in the world by the number of languages they contain, each having roughly one-fifth of the total languages counted in the world. The geographical span of Austronesian was the largest of any language family before the spread of Indo-European in the colonial period, ranging from Madagascar off the southeastern coast of Africa to Easter Island in the eastern Pacific. Hawaiian, Rapa Nui, and Malagasy (spoken on Madagascar) are the geographic outliers of the Austronesian family.
According to Robert Blust (1999), Austronesian is divided in several primary branches, all but one of which are found exclusively on Taiwan. The Formosan languages of Taiwan are grouped into as many as nine first-order subgroups of Austronesian. All Austronesian languages spoken outside Taiwan (including its offshore Yami language) belong to the Malayo-Polynesian branch, sometimes called Extra-Formosan.
Most Austronesian languages lack a long history of written attestation, making the feat of reconstructing earlier stages – up to distant Proto-Austronesian – all the more remarkable. The oldest inscription in the Cham language, the Đông Yên Châu inscription, but with the influence of Indo-European languages, dated to the mid-6th century AD at the latest, is also the first attestation of any Austronesian language.
Contents
Structure[edit]

It is difficult to make generalizations about the languages that make up a family as diverse as Austronesian. Very broadly, one can divide the Austronesian languages into three groups: Philippine-type languages, Indonesian-type languages and post-Indonesian type languages (Ross 2002):
- The first group includes, besides the languages of the Philippines, the Austronesian languages of Taiwan, Sabah, North Sulawesi and Madagascar. It is primarily characterized by the retention of the original system of Philippine-type voice alternations, where typically three or four verb voices determine which semantic role the "subject"/"topic" expresses (it may express either the actor, the patient, the location and the beneficiary, or various other circumstantial roles such as instrument and concomitant). The phenomenon has frequently been referred to as focus (not to be confused with the usual sense of that term in linguistics). Furthermore, the choice of voice is influenced by the definiteness of the participants. The word order has a strong tendency to be verb-initial.
- In contrast, the more innovative Indonesian-type languages, which are particularly represented in Malaysia and western Indonesia, have reduced the voice system to a contrast between only two voices (actor voice and "undergoer" voice), but these are supplemented by applicative morphological devices (originally two: the more direct *-i and more oblique *-an/-[a]kən), which serve to modify the semantic role of the "undergoer". They are also characterized by the presence of preposed clitic pronouns. Unlike the Philippine type, these languages mostly tend towards verb-second word-orders. A number of languages, such as the Batak languages, Old Javanese, Balinese, Sasak and several Sulawesi languages seem to represent an intermediate stage between these two types.[7][8]
- Finally, in some languages, which Ross calls "post-Indonesian", the original voice system has broken down completely and the voice-marking affixes no longer preserve their functions.
The Austronesian languages tend to use reduplication (repetition of all or part of a word, as in wiki-wiki or agar-agar). Like many East and Southeast Asian languages, most Austronesian languages have highly restrictive phonotactics, with generally small numbers of phonemes and predominantly consonant–vowel syllables.
Lexicon[edit]
The Austronesian language family has been established by the linguistic comparative method on the basis of cognate sets, sets of words similar in sound and meaning which can be shown to be descended from the same ancestral word in Proto-Austronesian according to regular rules. Some cognate sets are very stable. The word for eye in many Austronesian languages is mata (from the most northerly Austronesian languages, Formosan languages such as Bunun and Amis all the way south to Māori). Other words are harder to reconstruct. The word for two is also stable, in that it appears over the entire range of the Austronesian family, but the forms (e.g. Bunun dusa; Amis tusa; Māori rua) require some linguistic expertise to recognise. The Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database gives word lists (coded for cognateness) for approximately 1000 Austronesian languages.
Classification[edit]
The internal structure of the Austronesian languages is complex. The family consists of many similar and closely related languages with large numbers of dialect continua, making it difficult to recognize boundaries between branches. However, it is clear that the greatest genealogical diversity is found among the Formosan languages of Taiwan, and the least diversity among the islands of the Pacific, supporting a dispersal of the family from Taiwan or China. The first comprehensive classification to reflect this was Dyen (1965).
The seminal article in the classification of Formosan—and, by extension, the top-level structure of Austronesian—is Blust (1999). Prominent Formosanists (linguists who specialize in Formosan languages) take issue with some of its details, but it remains the point of reference for current linguistic analyses, and is shown below. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are frequently included within Blust's Eastern Formosan branch due to their shared leveling of proto-Austronesian *t, *C to /t/ and *n, *N to /n/, their shift of *S to /h/, and vocabulary such as *lima "five" which are not attested in other Formosan languages.
There appear to have been two great migrations of Austronesian languages that quickly covered large areas, resulting in multiple local groups with little large-scale structure. The first was Malayo-Polynesian, distributed across the Philippines, Indonesia, and Melanesia. The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages are similar to each other not because of close genealogical relationships, but rather because they reflect strong substratum effects from non-Austronesian languages. The second migration was that of the Oceanic languages into Polynesia and Micronesia (Greenhill, Blust & Gray 2008).
In addition to Malayo-Polynesian, thirteen Formosan families are broadly accepted. Debate centers primarily around the relationships between these families. Of the classifications presented here, Blust (1999) links two families into a Western Plains group, two more in a Northwestern Formosan group, and three into an Eastern Formosan group, while Lee (2008)[citation not found] also links five families into a Northern Formosan group. The Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database (2008) accepts Northern, rejects Eastern, links Tsouic and Rukai (two highly divergent languages), and links Malayo-Polynesian with Paiwan in a Paiwanic group. Ross (2009) splits Tsouic, and notes that Tsou, Rukai, and Puyuma fall outside of reconstructions of Proto-Austronesian.
Other studies have presented phonological evidence for a reduced Paiwanic family of Paiwanic, Puyuma, Bunun, Amis, and Malayo-Polynesian, but this is not reflected in vocabulary. The Eastern Formosan peoples Basay, Kavalan, and Amis share a homeland motif that has them coming originally from an island called Sinasay or Sanasay (Li 2004). The Amis, in particular, maintain that they came from the east, and were treated by the Puyuma, amongst whom they settled, as a subservient group.[9]
Blust (1999)[edit]
- Austronesian
(clockwise from the southwest)
- Thao language, AKA Sao. Brawbaw and Shtafari dialects.
- Central Western Plains
- Babuza language: Taokas, Poavosa dialects; old Favorlang language.
- Papora-Hoanya language: Papora, Hoanya dialects.
- Saisiyat language: Taai and Tungho dialects.
- Pazeh language AKA Kulun.
- Atayal language.
- Seediq language: AKA Truku/Taroko.
- Northern (Kavalanic languages).
- Basay language: Trobiawa and Linaw–Qauqaut dialects.
- Kavalan language.
- Ketagalan language, or Ketangalan.
- Central (Ami).
- Siraya language.
- Mantauran, Tona, and Maga dialects of Rukai are divergent.
Li (2008)[edit]
This classification retains Blust's East Formosan, and unites the other northern languages. Li proposes a Proto-Formosan (F0) ancestor and equates it with Proto-Austronesian (PAN), following the model in Starosta (1995).[10][11] Rukai and Tsouic are seen as highly divergent,[10] although the position of Rukai is highly controversial.[12]
- F0: Formosan = Austronesian
Ross (2009)[edit]
In 2009, Malcolm Ross proposed a new classification of the Austronesian language family based on morphological evidence from various Formosan languages.[13] He proposed that the current reconstructions for Proto-Austronesian actually correspond to an intermediate stage, which he terms "Proto-Nuclear Austronesian". Notably, Ross' classification does not support the unity of the Tsouic languages, instead considering the Southern Tsouic languages of Kanakanavu and Saaroa to be a separate branch. This supports Chang's (2006) claim that Tsouic is not a valid group.[14]
- Austronesian
- (Mantauran and Tona–Maga dialects are divergent)
- Subdivisions not addressed, apart from Saaroa–Kanakanabu being separate from Tsou.
Major languages[edit]
History[edit]
The protohistory of the Austronesian people can be traced farther back through time than can that of the Proto-Austronesian language. From the standpoint of historical linguistics, the home (in linguistic terminology, Urheimat) of the Austronesian languages is the main island of Taiwan, also known as Formosa; on this island the deepest divisions in Austronesian are found, among the families of the native Formosan languages. According to Robert Blust, the Formosan languages form nine of the ten primary branches of the Austronesian language family (Blust 1999). Comrie (2001:28) noted this when he wrote:
... the internal diversity among the... Formosan languages... is greater than that in all the rest of Austronesian put together, so there is a major genetic split within Austronesian between Formosan and the rest... Indeed, the genetic diversity within Formosan is so great that it may well consist of several primary branches of the overall Austronesian family.
At least since Sapir (1968), linguists have generally accepted that the chronology of the dispersal of languages within a given language family can be traced from the area of greatest linguistic variety to that of the least. For example, English in North America has large numbers of speakers, but relatively low dialectal diversity, while English in Great Britain has much higher diversity; such low linguistic variety by Sapir's thesis suggests a more recent origin of English in North America. While some scholars suspect that the number of principal branches among the Formosan languages may be somewhat less than Blust's estimate of nine (e.g. Li 2006), there is little contention among linguists with this analysis and the resulting view of the origin and direction of the migration. For a recent dissenting analysis, see (Peiros 2004). To get an idea of the original homeland of the Austronesian people, scholars can probe evidence from archaeology and genetics. Studies from the science of genetics have produced conflicting outcomes. Some researchers find evidence for a proto-Austronesian homeland on the Asian mainland (e.g., Melton et al. 1998), while others mirror the linguistic research, rejecting an East Asian origin in favor of Taiwan (e.g., Trejaut et al. 2005). Archaeological evidence (e.g., Bellwood 1997) is more consistent, suggesting that the ancestors of the Austronesians spread from the South Chinese mainland to Taiwan at some time around 8,000 years ago. Evidence from historical linguistics suggests that it is from this island that seafaring peoples migrated, perhaps in distinct waves separated by millennia, to the entire region encompassed by the Austronesian languages (Diamond 2000). It is believed that this migration began around 6,000 years ago (Blust 1999). However, evidence from historical linguistics cannot bridge the gap between those two periods. The view that linguistic evidence connects Austronesian languages to the Sino-Tibetan ones, as proposed for example by Sagart (2002), is a minority one. As Fox (2004:8) states:
Implied in... discussions of subgrouping [of Austronesian languages] is a broad consensus that the homeland of the Austronesians was in Taiwan. This homeland area may have also included the P'eng-hu (Pescadores) islands between Taiwan and China and possibly even sites on the coast of mainland China, especially if one were to view the early Austronesians as a population of related dialect communities living in scattered coastal settlements.
Linguistic analysis of the Proto-Austronesian language stops at the western shores of Taiwan; any related mainland language(s) have not survived. The only exceptions, the Chamic languages, derive from more recent migration to the mainland (Thurgood 1999:225).
Hypothesized relations[edit]
Genealogical links have been proposed between Austronesian and various families of East and Southeast Asia.
Austric[edit]
A link with the Austroasiatic languages in an 'Austric' phylum is based mostly on typological evidence. However, there is also morphological evidence of a connection between the conservative Nicobarese languages and Austronesian languages of the Philippines. Paul K. Benedict extended the Austric proposal to include Kra-Dai-Japanese and Hmong–Mien families, but this is still controversial and the Austric family stays as hypothetical family only.
Austro-Tai[edit]
A competing Austro-Tai proposal linking Austronesian and Tai–Kadai is supported by Weera Ostapirat, Roger Blench, and Laurent Sagart, and is based on the traditional comparative method. Ostapirat (2005) proposes a series of regular correspondences linking the two families and assumes a primary split, with Tai–Kadai speakers being the Austronesians who stayed behind in their Chinese homeland. Blench (2004) suggests that, if the connection is valid, the relationship is unlikely to be one of two sister families. Rather, he suggests that proto-Tai–Kadai speakers were Austronesians who migrated to Hainan Island and back to the mainland from the northern Philippines, and that their distinctiveness results from radical restructuring following contact with Hmong–Mien and Sinitic.
Kosaka (2002) suggests that similarities between Kra-Dai and Austronesian are because of later areal contact in coastal arear of eastern and southeastern China. Instead, he speculates about a common origin between Hmong-Mien and Kra-Dai.[15]
Sino-Austronesian[edit]
French linguist and Sinologist Laurent Sagart considers the Austronesian languages to be related to the Sino-Tibetan languages, and also groups the Tai–Kadai languages as more closely related to the Malayo-Polynesian languages.[16] He also groups the Austronesian languages in a recursive-like fashion, placing Tai–Kadai as a sister branch of Malayo-Polynesian. His methodology has been found to be spurious by his peers.
Japanese[edit]
Several linguists have proposed that Japanese may be a relative of the Austronesian family.[17] Some linguists think it is more plausible that Japanese might have instead been influenced by Austronesian languages, perhaps by an Austronesian substratum. Those who propose this scenario suggest that the Austronesian family once covered the islands to the north as well as to the south. Alexander Vovin calls his reconstruction of Proto-Japanese suggestive of a Southeast Asian origin of the Japonic languages, but does not support or is unsure about a direct relation to Austronesian.[18] Several Japanese linguists classify Japanese as "Para-Austronesian".[citation needed]
Ongan[edit]
It has recently been proposed that the Austronesian and the Ongan protolanguage are the descendants of an Austronesian–Ongan protolanguage (Blevins 2007).[19] But this view is not supported by mainstream linguists and remains very controversial. Robert Blust (2014) rejects Blevins' proposal as far-fetched and based solely on chance resemblances and methodologically flawed comparisons.[20]
Writing systems[edit]
Most Austronesian languages have Latin-based writing systems today. Some non-Latin-based writing systems are listed below.
- Brahmi script
- Kawi script
- Balinese alphabet - used to write Balinese and Sasak.
- Batak alphabet - used to write several Batak languages.
- Baybayin - used to write Tagalog and several Philippine languages.
- Bima alphabet - once used to write the Bima language.
- Buhid alphabet - used to write Buhid language.
- Hanunó'o alphabet - used to write Hanuno'o language.
- Javanese alphabet - used to write the Javanese language and several neighbouring languages like Madurese.
- Kerinci alphabet (Kaganga) - used to write the Kerinci language.
- Kulitan alphabet - used to write the Kapampangan language.
- Lampung alphabet - used to write Lampung and Komering.
- Lontara alphabet - used to write the Buginese, Makassarese and several languages of Sulawesi.
- Sundanese alphabet - used to write the Sundanese language.
- Rejang alphabet - used to write the Rejang language.
- Rencong alphabet - once used to write the Malay language.
- Tagbanwa alphabet - once used to write various Palawan languages.
- Lota alphabet - used to write the Ende-Li'o language.
- Cham alphabet - used to write Cham language.
- Kawi script
- Arabic script
- Pegon alphabet - used to write Javanese, Sundanese and Madurese as well as several smaller neighbouring languages.
- Jawi alphabet - used to write Malay, Acehnese, Banjar, Minangkabau, Tausug, Western Cham and others.
- Sorabe alphabet - once used to write several dialects of Malagasy language.
- Hangul - once used to write the Cia-Cia language but the project is no longer active.
- Dunging - used to write the Iban language but it was not widely used.
- Avoiuli - used to write the Raga language.
- Eskayan - used to write the Eskayan language, a secret language based on Boholano.
- Woleai script (Caroline Island script) - used to write the Carolinian language (Refaluwasch).
- Rongorongo - possibly used to write the Rapa Nui language.
- Braille - used in Filipino, Malaysian, Indonesian, Tolai, Motu, Māori, Samoan, Malagasy, and many other Austronesian languages.
Comparison chart[edit]
Below is a chart comparing list of numbers of 1-10 and thirteen words in Austronesian languages; spoken in Taiwan, the Philippines, the Mariana Islands, Indonesia, Malaysia, Chams or Champa (in Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam), East Timor, Papua, New Zealand, Hawaii, Madagascar, Borneo and Tuvalu.
Comparison chart-numerals[edit]
| Austronesian List of Numbers 1-10 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-Austronesian | *əsa *isa |
*duSa | *təlu | *Səpat | *lima | *ənəm | *pitu | *walu | *Siwa | *(sa-)puluq | |||||||||||
| Formosan languages | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Atayal | qutux | sazing | cyugal | payat | magal | mtzyu | mpitu | mspat | mqeru | mopuw | |||||||||||
| Seediq | kingal | daha | teru | sepac | rima | mmteru | mpitu | mmsepac | mngari | maxal | |||||||||||
| Truku | kingal | dha | tru | spat | rima | mataru | empitu | maspat | mngari | maxal | |||||||||||
| Thao | taha | tusha | turu | shpat | tarima | katuru | pitu | kashpat | tanathu | makthin | |||||||||||
| Papora | tanu | nya | tul | pat | lima | minum | pitu | mehal | mesi | metsi | |||||||||||
| Babuza | nata | naroa | natura | naspat | nahop | naitu | naito | natap | maitu | tsihet | |||||||||||
| Taokas | tatanu | rua | tool'a | lapat | hasap | tahap | yuweto | mahalpat | tanaso | tais'id | |||||||||||
| Pazeh | adang | dusa | tu'u | supat | xasep | xasebuza | xasebidusa | xasebitu'u | xasebisupat | isit | |||||||||||
| Saisiyat | 'aeihae' | roSa' | to:lo' | Sopat | haseb | SayboSi: | SayboSi: 'aeihae' | maykaSpat | hae'hae' | lampez | |||||||||||
| Tsou | coni | yuso | tuyu | sʉptʉ | eimo | nomʉ | pitu | voyu | sio | maskʉ | |||||||||||
| Bunun | tasʔa | dusa | tau | paat | hima | nuum | pitu | vau | siva | masʔan | |||||||||||
| Rukai | itha | drusa | tulru | supate | lrima | eneme | pitu | valru | bangate | pulruku | |||||||||||
| Paiwan | ita | drusa | tjelu | sepatj | lima | enem | pitju | alu | siva | tapuluq | |||||||||||
| Puyuma | isa | zuwa | telu | pat | lima | unem | pitu | walu | iwa | pulu' | |||||||||||
| Kavalan | usiq | uzusa | utulu | uspat | ulima | unem | upitu | uwalu | usiwa | rabtin | |||||||||||
| Basay | tsa | lusa | tsu | səpat | tsjima | anəm | pitu | wasu | siwa | labatan | |||||||||||
| Amis | cecay | tosa | tolo | spat | lima | enem | pito | falo | siwa | mo^tep | |||||||||||
| Sakizaya | cacay | tosa | tolo | sepat | lima | enem | pito | walo | siwa | cacay a bataan | |||||||||||
| Siraya | sasaat | duha | turu | tapat | tu-rima | tu-num | pitu | pipa | kuda | keteng | |||||||||||
| Taivoan | tsaha' | ruha | toho | paha' | hima | lom | kito' | kipa' | matuha | kaipien | |||||||||||
| Makatao | na-saad | ra-ruha | ra-ruma | ra-sipat | ra-lima | ra-hurum | ra-pito | ra-haru | ra-siwa | ra-kaitian | |||||||||||
| Yami | asa | dora | atlo | apat | lima | anem | pito | wao | siyam | poo | |||||||||||
| Qauqaut | is | zus | dor | sop | rim | ən | pit | ar | siu | tor | |||||||||||
| Malayo-Polynesian languages | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Proto-Malayo-Polynesian | *əsa *isa |
*duha | *təlu | *əpat | *lima | *ənəm | *pitu | *walu | *siwa | *puluq | |||||||||||
| Nuclear Malayo-Polynesian (MP) languages | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Acehnese | sifar soh |
sa | duwa | lhee | peuet | limong | nam | tujoh | lapan | sikureueng | siploh | ||||||||||
| Balinesea | nul |
besik siki |
dua |
telu |
papat |
lime |
nenem |
pitu |
kutus |
sia |
dasa | ||||||||||
| Banjar | asa | dua | talu | ampat | lima | anam | pitu | walu | sanga | sapuluh | |||||||||||
| Batak, Toba | sada | dua | tolu | opat | lima | onom | pitu | ualu | sia | sampulu | |||||||||||
| Buginese | ceddi | dua | tellu | empa | lima | enneng | pitu | arua | asera | seppulo | |||||||||||
| Cia-Cia | 디세 dise ise |
루아 rua ghua |
똘루 tolu |
빠아 pa'a |
을리마 lima |
노오 no'o |
삐쭈 picu |
ᄫᅡᆯ루 walu oalu |
시우아 siua |
옴뿔루 ompulu | |||||||||||
| Cham | sa | dua | klau | pak | lima | nam | tujuh | dalapan | salapan | sapluh | |||||||||||
| Javanese (Kawi)b[21] | sunya | eka |
dwi |
tri |
catur |
panca |
sad |
sapta |
asta |
nawa |
dasa | ||||||||||
| Old Javanese[22] | das | sa (sa' / sak) |
rwa | tĕlu | pāt | lima | nĕm | pitu | walu | sanga | sapuluh | ||||||||||
| Javanese (Krama) | nol | setunggal | kalih | tiga | sekawan | gangsal | enem | pitu | wolu | sanga | sedasa | ||||||||||
| Javanese (Ngoko)[23] | nol | siji from sahiji | loro from ka-rwa (ka-ro) | telu | papat | lima | enem | pitu | wolu | sanga | sepuluh | ||||||||||
| Kelantan-Pattani | kosong | so | duwo | tigo | pak | limo | ne | tujoh | lape | smile | spuloh | ||||||||||
| Madurese | nol | settong | dhuwa' | tello' | empa' | lema' | ennem | petto' | ballu' | sanga' | sapolo | ||||||||||
| Makassarese | ᨒᨚᨅ lobbang ᨊᨚᨒᨚ nolo' |
ᨙᨔᨙᨑ se're |
ᨑᨘᨕ rua |
ᨈᨒᨘ tallu |
ᨕᨄ appa' |
ᨒᨗᨆ lima |
ᨕᨊ annang |
ᨈᨘᨍ tuju |
ᨔᨂᨈᨘᨍ sangantuju |
ᨔᨒᨄ salapang |
ᨔᨄᨘᨒᨚ sampulo | ||||||||||
| Standard Malay (both Indonesian and Malaysian) |
kosong sifar[24] nol[25] |
sa/se satu suatu[26] |
dua | tiga[27][28] | empat | lima[29] | enam | tujuh | delapan lapan[30] |
sembilan | sepuluh | ||||||||||
| Minangkabau | ciek | duo | tigo | ampek | limo | anam | tujuah | salapan | sambilan | sapuluah | |||||||||||
| Moken | cha:? | thuwa:? | teloj (təlɔy) |
pa:t | lema:? | nam | luɟuːk | waloj (walɔy) |
chewaj (cʰɛwaːy / sɛwaːy) |
cepoh | |||||||||||
| Sasak | sekek | due | telo | empat | lime | enam | pituk | baluk | siwak | sepulu | |||||||||||
| Sundanese | ᮔᮧᮜ᮪ nol |
ᮠᮤᮏᮤ hiji |
ᮓᮥᮃ dua |
ᮒᮤᮜᮥ tilu |
ᮇᮕᮒ᮪ opat |
ᮜᮤᮙ lima |
ᮌᮨᮔᮨᮕ᮪ genep |
ᮒᮥᮏᮥᮂ tujuh |
ᮓᮜᮕᮔ᮪ dalapan |
ᮞᮜᮕᮔ᮪ salapan |
ᮞᮕᮥᮜᮥᮂ sapuluh | ||||||||||
| Terengganu Malay | kosong | se | duwe | tige | pak | lime | nang | tujoh | lapang | smilang | spuloh | ||||||||||
| Tetun | nol | ida | rua | tolu | hat | lima | nen | hitu | ualu | sia | sanulu | ||||||||||
| Tsat (HuiHui)c | sa˧ * ta˩ ** |
tʰua˩ | kiə˧ | pa˨˦ | ma˧ | naːn˧˨ | su˥ | paːn˧˨ | tʰu˩ paːn˧˨ | piu˥ | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Borneo–Philippine languages | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Ilocano | ibbong awan |
maysa | dua | tallo | uppat | lima | innem | pito | walo | siam | sangapulo | ||||||||||
| Ibanag | awan | tadday | duwa | tallu | appa' | lima | annam | pitu | walu | siyam | mafulu | ||||||||||
| Pangasinan | sakey | duwa | talo | apat | lima | anem | pito | walo | siyam | samplo | |||||||||||
| Kapampangan | ala | metung/ isa' | adua | atlu | apat | lima | anam | pitu | walu | siyam | apulu | ||||||||||
| Tagalog | walâ |
isá |
dalawá |
tatló |
apat |
limá |
anim |
pitó |
waló |
siyám |
sampû | ||||||||||
| Bikol | wara | sarô | duwá | tuló | apat | limá | anom | pitó | waló | siyám | sampulû | ||||||||||
| Aklanon | uwa | isaea sambilog |
daywa | tatlo | ap-at | lima | an-om | pito | waeo | siyam | napueo | ||||||||||
| Karay-a | wara | (i)sara | darwa | tatlo | apat | lima | anəm | pito | walo | siyam | napulo | ||||||||||
| Onhan | isya | darwa | tatlo | upat | lima | an-om | pito | walo | siyam | sampulo | |||||||||||
| Romblomanon | isa | duha | tuyo | upat | lima | onum | pito | wayo | siyam | napuyo | |||||||||||
| Masbatenyo | isad usad |
duwa duha |
tulo | upat | lima | unom | pito | walo | siyam | napulo | |||||||||||
| Hiligaynon | wala | isa | duha | tatlo | apat | lima | anom | pito | walo | siyam | napulo | ||||||||||
| Cebuano | wala | usa | duha | tulo | upat | lima | unom | pito | walo | siyam | napulo pulo | ||||||||||
| Waray | waray | usa | duha | tulo | upat | lima | unom | pito | walo | siyam | napulò | ||||||||||
| Tausug | sipar | isa | duwa | tū | upat | lima | unum | pitu | walu | siyam | hangpu' | ||||||||||
| Maranao | isa | dua | telu | pat | lima | nem | pitu | ualu | siau | sapulu' | |||||||||||
| Benuaq (Dayak Benuaq) | eray | duaq | toluu | opaat | limaq | jawatn | turu | walo | sie | sepuluh | |||||||||||
| Lun Bawang/ Lundayeh | na luk dih | eceh | dueh | teluh | epat | limeh | enem | tudu' | waluh | liwa' | pulu' | ||||||||||
| Dusun | aiso | iso | duo | tolu | apat | limo | onom | turu | walu | siam | hopod | ||||||||||
| Malagasy | aotra | isa iray |
roa | telo | efatra | dimy | enina | fito | valo | sivy | folo | ||||||||||
| Sangirese (Sangir-Minahasan) | sembau | darua | tatelu | epa | lima | eneng | pitu | walu | sio | mapulo | |||||||||||
| Oceanic languagesd | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Fijian | saiva | dua | rua | tolu | vaa | lima | ono | vitu | walu | ciwa | tini | ||||||||||
| Hawaiian | 'ole | 'e-kahi | 'e-lua | 'e-kolu | 'e-hā | 'e-lima | 'e-ono | 'e-hiku | 'e-walu | 'e-iwa | 'umi | ||||||||||
| Kiribati | akea | teuana | uoua | tenua | aua | nimaua | onoua | itua | wanua | ruaiwa | tebwina | ||||||||||
| Māori | kore | tahi | rua | toru | whā | rima | ono | whitu | waru | iwa | tekau ngahuru | ||||||||||
| Marshallese[31] | o̧o | juon | ruo | jilu | emān | ļalem | jiljino | jimjuon | ralitōk | ratimjuon | jon̄oul | ||||||||||
| Motue[32] | ta | rua | toi | hani | ima | tauratoi | hitu | taurahani | taurahani-ta | gwauta | |||||||||||
| Niuean | nakai | taha | ua | tolu | fa | lima | ono | fitu | valu | hiva | hogofulu | ||||||||||
| Rapanui | tahi | rua | toru | hā | rima | ono | hitu | va'u | iva | angahuru | |||||||||||
| Rarotongan Māori | kare | ta'i | rua | toru | 'ā | rima | ono | 'itu | varu | iva | nga'uru | ||||||||||
| Rotuman | ta | rua | folu | hake | lima | ono | hifu | vạlu | siva | saghulu | |||||||||||
| Sāmoan | o | tasi | lua | tolu | fa | lima | ono | fitu | valu | iva | sefulu | ||||||||||
| Sāmoan (K-type) |
o | kasi | lua | kolu | fa | lima | ogo | fiku | valu | iva | sefulu | ||||||||||
| Tahitian | hō'ē tahi |
piti | toru | maha | pae | ōno | hitu | va'u | iva | hō'ē 'ahuru | |||||||||||
| Tongan | noa | taha | ua | tolu | fa | nima | ono | fitu | valu | hiva | hongofulu taha noa | ||||||||||
| Trukese | eet | érúúw | één | fáán | niim | woon | fúús | waan | ttiw | engoon | |||||||||||
| Tuvaluan | tahi tasi |
lua | tolu | fa | lima | ono | fitu | valu | iva | sefulu | |||||||||||
Comparison chart-thirteen words[edit]
| English | one | two | three | four | person | house | dog | road | day | new | we | what | fire |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-Austronesian | *əsa, *isa | *duSa | *təlu | *əpat | *Cau | *balay, *Rumaq | *asu | *zalan | *qaləjaw, *waRi | *baqəRu | *kita, *kami | *anu, *apa | *Sapuy |
| Tetum | ida | rua | tolu | haat | ema | uma | asu | dalan | loron | foun | ita | saida | ahi |
| Amis | cecay | tosa | tolo | sepat | tamdaw | luma | wacu | lalan | cidal | faroh | kita | uman | namal |
| Puyuma | sa | dua | telu | pat | taw | rumah | soan | dalan | wari | vekar | mi | amanai | apue, asi |
| Tagalog | isa | dalawa | tatlo | apat | tao | bahay | aso | daan | araw | bago | tayo / kami | ano | apoy |
| Bikol | sarô | duwá | tuló | apat | táwo | harong | áyam | dálan | aldaw | bâgo | kitá | anó | kalayó |
| Rinconada Bikol | əsad | darwā | tolō | əpat | tawō | baləy | ayam | raran | aldəw | bāgo | kitā | onō | kalayō |
| Waray | usa | duha | tulo | upat | tawo | balay | ayam, ido |
dalan | adlaw | bag-o | kita | anu | kalayo |
| Cebuano | usa, isa |
duha | tulo | upat | tawo | balay | iro | dalan | adlaw | bag-o | kita | unsa | kalayo |
| Hiligaynon | isa | duha | tatlo | apat | tawo | balay | ido | dalan | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo |
| Aklanon | isaea, sambilog |
daywa | tatlo | ap-at | tawo | baeay | ayam | daean | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kaeayo |
| Kinaray-a | (i)sara | darwa | tatlo | apat | tawo | balay | ayam | dalan | adlaw | bag-o | kita | ano | kalayo |
| Tausug | hambuuk | duwa | tu | upat | tau | bay | iru' | dan | adlaw | ba-gu | kitaniyu | unu | kayu |
| Maranao | isa | dowa | t'lo | phat | taw | walay | aso | lalan | gawi'e | bago | tano | tonaa | apoy |
| Kapampangan | metung | adwa | atlu | apat | tau | bale | asu | dalan | aldo | bayu | ikatamu | nanu | api |
| Pangasinan | sakey | dua, duara |
talo, talora |
apat, apatira |
too | abong | aso | dalan | ageo | balo | sikatayo | anto | pool |
| Ilokano | maysa | dua | tallo | uppat | tao | balay | aso | dalan | aldaw | baro | datayo | ania | apoy |
| Ivatan | asa | dadowa | tatdo | apat | tao | vahay | chito | rarahan | araw | va-yo | yaten | ango | apoy |
| Ibanag | tadday | dua | tallu | appa' | tolay | balay | kitu | dalan | aggaw | bagu | sittam | anni | afi |
| Yogad | tata | addu | tallu | appat | tolay | binalay | atu | daddaman | agaw | bagu | sikitam | gani | afuy |
| Gaddang | antet | addwa | tallo | appat | tolay | balay | atu | dallan | aw | bawu | ikkanetam | sanenay | afuy |
| Tboli | sotu | lewu | tlu | fat | tau | gunu | ohu | lan | kdaw | lomi | tekuy | tedu | ofih |
| Lun Bawang/ Lundayeh | eceh | dueh | teluh | epat | lemulun/lun | ruma' | uko' | dalan | eco | beruh | teu | enun | apui |
| Malay | sa/se, satu, suatu |
dua | tiga[33] | empat | orang | rumah, balai |
anjing | jalan | hari | baru | kita | apa, anu |
api |
| Old Javanese | esa, eka |
rwa, dwi |
tĕlu, tri |
pat, catur[34] |
wwang | umah | asu | dalan | dina | hañar, añar[35] | kami[36] | apa, aparan |
apuy, agni |
| Javanese | siji, setunggal |
loro, kalih |
tĕlu, tiga[37] |
papat, sekawan |
uwong, tiyang, priyantun[37] |
omah, griya, dalem[37] |
asu, sĕgawon |
dalan, gili[37] |
dina, dinten[37] |
anyar, énggal[37] |
awaké dhéwé, kula panjenengan[37] |
apa, punapa[37] |
gĕni, latu, brama[37] |
| Sundanese | hiji | dua | tilu | opat | urang | imah | anjing | jalan | poe | anyar, enggal |
arurang | naon | seuneu |
| Acehnese | sa | duwa | lhèë | peuët | ureuëng | rumoh, balè, seuëng |
asèë | röt | uroë | barô | (geu)tanyoë | peuë | apui |
| Minangkabau | ciek | duo | tigo | ampek | urang | rumah | anjiang | labuah, jalan |
hari | baru | awak | apo | api |
| Lampungese | sai | khua | telu | pak | jelema | lamban | kaci | ranlaya | khani | baru | kham | api | apui |
| Buginese | se'di | dua | tellu | eppa' | tau | bola | asu | laleng | esso | baru | idi' | aga | api |
| Temuan | satuk | duak | tigak | empat | uwang, eang |
gumah, umah |
anying, koyok |
jalan | aik, haik |
bahauk | kitak | apak | apik |
| Toba Batak | sada | dua | tolu | opat | halak | jabu | biang | dalan | ari | baru | hita | aha | api |
| Kelantan-Pattani | so | duwo | tigo | pak | oghe | ghumoh, dumoh |
anjing | jale | aghi | baghu | kito | gapo | api |
| Chamorro | håcha, maisa |
hugua | tulu | fatfat | taotao/tautau | guma' | ga'lågu[38] | chålan | ha'åni | nuebu[39] | hita | håfa | guåfi |
| Motu | ta, tamona |
rua | toi | hani | tau | ruma | sisia | dala | dina | matamata | ita, ai |
dahaka | lahi |
| Māori | tahi | rua | toru | whā | tangata | whare | kurī | ara | rā | hou | tāua, tātou/tātau māua, mātou/mātau |
aha | ahi |
| Tuvaluan | tasi | lua | tolu | fá | toko | fale | kuli | ala, tuu |
aso | fou | tāua | a | afi |
| Hawaiian | kahi | lua | kolu | hā | kanaka | hale | 'īlio | ala | ao | hou | kākou | aha | ahi |
| Banjarese | asa | duwa | talu | ampat | urang | rūmah | hadupan | heko | hǎri | hanyar | kami | apa | api |
| Malagasy | isa | roa | telo | efatra | olona | trano | alika | lalana | andro | vaovao | isika | inona | afo |
| Dusun | iso | duo | tolu | apat | tulun | walai, lamin |
tasu | ralan | tadau | wagu | tokou | onu/nu | tapui |
| Kadazan | iso | duvo | tohu | apat | tuhun | hamin | tasu | lahan | tadau | vagu | tokou | onu, nunu |
tapui |
| Rungus | iso | duvo | tolu, tolzu |
apat | tulun, tulzun |
valai, valzai |
tasu | dalan | tadau | vagu | tokou | nunu | tapui, apui |
| Sungai/Tambanuo | ido | duo | tolu | opat | lobuw | waloi | asu | ralan | runat | wagu | toko | onu | apui |
| Iban | satu, sa, siti, sigi |
dua | tiga | empat | orang, urang |
rumah | ukui, uduk |
jalai | hari | baru | kitai | nama | api |
| Sarawak Malay | satu, sigek |
dua | tiga | empat | orang | rumah | asuk | jalan | ari | baru | kita | apa | api |
| Terengganuan | se | duwe | tige | pak | oghang | ghumoh, dumoh |
anjing | jalang | aghi | baghu | kite | mende, ape, gape, nape |
api |
| Kanayatn | sa | dua | talu | ampat | urakng | rumah | asu' | jalatn | ari | baru | kami', diri' |
ahe | api |
See also[edit]
- Ainu languages
- Austric languages
- Austronesia
- Austronesian Formal Linguistics Association
- Austronesian peoples
- Domesticated plants and animals of Austronesia
- Austro-Tai
- Hmong-Mien
- Indonesian language and Malaysian language
- Japanese language
- List of Austronesian languages
- List of Austronesian regions
- Margaret Florey
- Tai-Kadai
Notes[edit]
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Austronesian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ^ "Austronesian Languages". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- ^ Blust, Robert (2016). History of the Austronesian Languages. University of Hawaii at Manoa.
- ^ Asya Pereltsvaig (2018). Languages of the World. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-316-62196-7.
- ^ Dempwolff, Otto (1934-37). Vergleichende Lautlehre des austronesischen Wortschatzes. (Beihefte zur Zeitschrift für Eingeborenen-Sprachen 15;17;19). Berlin: Dietrich Reimer. (3 vols.)
- ^ John Simpson; Edmund Weiner, eds. (1989). Official Oxford English Dictionary (OED2) (Dictionary). Oxford University Press. p. 22000..
- ^ Adelaar, K. Alexander and Nikolaus Limmelmann. 2005. The Austronesian Languages of Asia and Madagascar. P.6-7
- ^ Croft, William. 2012 Verbs: Aspect and Causal Structure. P.261
- ^ Taylor, G. (1888). "A ramble through southern Formosa". The China Review. 16: 137–161.
The Tipuns... are certainly descended from emigrants, and I have not the least doubt but that the Amias are of similar origin; only of later date, and most probably from the Mejaco Simas [that is, Miyako-jima], a group of islands lying 110 miles to the North-east.... By all accounts the old Pilam savages, who merged into the Tipuns, were the first settlers on the plain; then came the Tipuns, and a long time afterwards the Amias. The Tipuns, for some time, acknowledged the Pilam Chief as supreme, but soon absorbed both the chieftainship and the people, in fact the only trace left of them now, is a few words peculiar to the Pilam village, one of which, makan (to eat), is pure Malay. The Amias submitted themselves to the jurisdiction of the Tipuns.
- ^ a b Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 2008. "Time perspective of Formosan Aborigines." In Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia ed. Past human migrations in East Asia: matching archaeology, linguistics and genetics. Taylor & Francis US.
- ^ Starosta, S. 1995. "A grammatical subgrouping of Formosan languages." In P. Li, Cheng-hwa Tsang, Ying-kuei Huang, Dah-an Ho, and Chiu-yu Tseng eds. Austronesian Studies Relating to Taiwan, pp. 683–726, Taipei: Institute of History and Philology, Academia Sinica.
- ^ "The position of Rukai is the most controversial: Tsuchida... treats it as more closely related to Tsouic languages, based on lexicostatistic evidence, while Ho... believes it to be one of the Paiwanic languages, i.e. part of my Southern group, as based on a comparison of fourteen grammatical features. In fact, Japanese anthropologists did not distinguish between Rukai, Paiwan and Puyuma in the early stage of their studies" (Li 2008: 216).
- ^ Ross, Malcolm. 2009. "Proto Austronesian verbal morphology: A reappraisal." In Alexander Adelaar and Andrew Pawley (eds.). Austronesian historical linguistics and culture history: a festschrift for Robert Blust. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- ^ Chang, Henry Yungli. 2006. "Rethinking the Tsouic Subgroup Hypothesis: A Morphosyntactic Perspective." In Chang, H., Huang, L. M., Ho, D. (eds.). Streams converging into an ocean: Festschrift in honor of Professor Paul Jen-Kuei Li on his 70th birthday. Taipei: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.
- ^ Kosaka, Ryuichi. 2002. "On the affiliation of Miao-Yao and Kadai: Can we posit the Miao-Dai family." Mon-Khmer Studies 32:71-100.
- ^ van Driem, George. 2005. Sino-Austronesian vs. Sino-Caucasian, Sino-Bodic vs. Sino-Tibetan, and Tibeto-Burman as default theory. Contemporary Issues in Nepalese Linguistics, pp. 285–338. "新网阻断页" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-26. Retrieved 2010-10-29. (see page 304)
- ^ Benedict (1990), Lewin (1976), Matsumoto (1975), Miller (1967), Murayama (1976), Shibatani (1990).
- ^ Vovin, Alexander. "Proto-Japanese beyond the accent system". Current Issues in Linguistic Theory: 141–156.
- ^ Blevins, Juliette (2007), "A Long Lost Sister of Proto-Austronesian? Proto-Ongan, Mother of Jarawa and Onge of the Andaman Islands" (PDF), Oceanic Linguistics, 46 (1): 154–198, doi:10.1353/ol.2007.0015, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-01-11
- ^ Robert Blust (2014) "Some Recent Proposals Concerning the Classification of the Austronesian Languages", Oceanic Linguistics 53:2:300–391.
- ^ Siman Widyatmanta, Adiparwa. Vol. I dan II. Cetakan Ketiga. Yogyakarta: U.P. "Spring", 1968.
- ^ Zoetmulder, P.J., Kamus Jawa Kuno-Indonesia. Vol. I-II. Terjemahan Darusuprapto-Sumarti Suprayitno. Jakarta: PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 1995.
- ^ [1] Javanese alphabet, pronunciation, and language (Aksara Jawa), http://www.omniglot.com/writing/javanese.htm
- ^ from the Arabic صِفْر ṣifr
- ^ Predominantly in Indonesia, comes from the Latin nullus
- ^ The Sanskrit loanword "Ekasila" : "Eka" means 1, "Sila" means "pillar", "principle" appeared in Sukarno's speech
- ^ In Kedukan Bukit inscription the numeral tlu ratus appears as three hundred, tlu as three, in http://www.wordsense.eu/telu/ the word telu is referred to as three in Malay, although the use of telu is very rare.
- ^ The Sanskrit loanword "Trisila" : "Tri" means 3, "Sila" means "pillar", "principle" appeared in Sukarno's speech
- ^ loanword from Sanskrit पञ्चन् páñcan - see Sukarno's Pancasila: "five principles", Pancawarna: "five colours, colourful".
- ^ lapan is a known contraction of delapan; predominant in Malaysia, Singapore and Brunei.
- ^ Cook, Richard (1992). Peace Corps Marshall Islands: Marshallese Language Training Manual (PDF), pg. 22. Accessed August 27, 2007
- ^ Percy Chatterton, (1975). Say It In Motu: An instant introduction to the common language of Papua. Pacific Publications. ISBN 978-0-85807-025-7
- ^ In Kedukan Bukit inscription appears the numeral Tlu ratus as Three hundred, Tlu as Three, in http://www.wordsense.eu/telu/ the word Telu is referred as Three in Malay and Indonesian Language although the use of Telu is very rare.
- ^ s.v. kawan, Old Javanese-English Dictionary, P.J. Zoetmulder and Stuart Robson, 1982
- ^ s.v. hañar, Old Javanese-English Dictionary, P.J. Zoetmulder and Stuart Robson, 1982
- ^ s.v. kami, this could mean both first person singular and plural, Old Javanese-English Dictionary, P.J. Zoetmulder and Stuart Robson, 1982
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Javanese English Dictionary, Stuart Robson and Singgih Wibisono, 2002
- ^ From Spanish "galgo"
- ^ From Spanish "nuevo"
References[edit]
- Bellwood, Peter (July 1991). "The Austronesian Dispersal and the Origin of Languages". Scientific American. 265 (1): 88–93. Bibcode:1991SciAm.265a..88B. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0791-88.
- Bellwood, Peter (1997). Prehistory of the Indo-Malaysian archipelago. Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press.
- Bellwood, Peter (1998). "Taiwan and the Prehistory of the Austronesians-speaking Peoples". Review of Archaeology. 18: 39–48.
- Bellwood, Peter; Fox, James; Tryon, Darrell (1995). The Austronesians: Historical and comparative perspectives. Department of Anthropology, Australian National University. ISBN 978-0-7315-2132-6.
- Bellwood, Peter & Alicia Sanchez-Mazas (June 2005). "Human Migrations in Continental East Asia and Taiwan: Genetic, Linguistic, and Archaeological Evidence". Current Anthropology. 46 (3): 480–484. doi:10.1086/430018.
- Blench, Roger (June 10–13, 2004). Stratification in the peopling of China: how far does the linguistic evidence match genetics and archaeology? (PDF). Human migrations in continental East Asia and Taiwan: genetic, linguistic and archaeological evidence. Geneva.
- Blevins, Juliette (2007). "A Long Lost Sister of Proto-Austronesian? Proto-Ongan, Mother of Jarawa and Onge of the Andaman Islands" (PDF). Oceanic Linguistics. 46 (1): 154–198. doi:10.1353/ol.2007.0015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-01-11.
- Blundell, David. "Austronesian Dispersal". Newsletter of Chinese Ethnology. 35: 1–26.
- Blust, Robert (1985). "The Austronesian Homeland: A Linguistic Perspective". Asian Perspectives. 26: 46–67.
- Blust, Robert (1999). "Subgrouping, circularity and extinction: some issues in Austronesian comparative". In Zeitoun, E.; Li, P.J.K. Selected papers from the Eighth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics. Taipei: Academia Sinica. pp. 31–94.
- Comrie, Bernard (2001). "Languages of the world". In Aronoff, Mark; Rees-Miller, Janie. The Handbook of LinguisticsLanguages of the world. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 19–42.
- Diamond, Jared M (2000). "Taiwan's gift to the world" (PDF). Nature. 403 (6771): 709–10. Bibcode:2000Natur.403..709D. doi:10.1038/35001685. PMID 10693781.
- Dyen, Isidore (1965). "A Lexicostatistical classification of the Austronesian languages". International Journal of American Linguistics (Memoir 19).
- Fox, James J. (19–20 August 2004). Current Developments in Comparative Austronesian Studies (PDF). Symposium Austronesia Pascasarjana Linguististik dan Kajian Budaya. Universitas Udayana, Bali.
- Fuller, Peter (2002). "Reading the Full Picture". Asia Pacific Research. Canberra, Australia: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies. Retrieved July 28, 2005.
- Greenhill, S.J.; Blust, R.; Gray, R.D (2008). "The Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database: From Bioinformatics to Lexomics". Evolutionary Bioinformatics. 4: 271–283. Archived from the original on 2017-04-21. Retrieved 2009-06-12..
- "Homepage of linguist Dr. Lawrence Reid". Retrieved July 28, 2005.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (2004). "Origins of the East Formosans:Basay, Kavalan, Amis, and Siraya". Language and Linguistics. 5 (2): 363–376.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (17–20 January 2006). The Internal Relationships of Formosan Languages (PDF). Tenth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics (ICAL). Puerto Princesa City, Palawan, Philippines.
- Lynch, John, Malcolm Ross and Terry Crowley (2002). The Oceanic languages. Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link)
- Melton T.; Clifford S.; Martinson J.; Batzer M. & Stoneking M. (1998). "Genetic evidence for the proto-Austronesian homeland in Asia: mtDNA and nuclear DNA variation in Taiwanese aboriginal tribes". American Journal of Human Genetics. 63 (6): 1807–23. doi:10.1086/302131. PMC 1377653. PMID 9837834.
- Ostapirat, Weera (2005). "Kra–Dai and Austronesian: Notes on phonological correspondences and vocabulary distribution". In Laurent Sagart, Roger Blench & Alicia Sanchez-Mazas. The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: Routledge Curzon. pp. 107–131.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
- Peiros, Ilia (June 10–13, 2004). Austronesian: What linguists know and what they believe they know. the workshop on Human migrations in continental East Asia and Taiwan. Geneva.
- Ross, Malcolm (2009). "Proto Austronesian verbal morphology: a reappraisal". In Adelaar, K. Alexander; Pawley, Andrew. Austronesian Historical Linguistics and Culture History: A Festschrift for Robert Blust. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 295–326.
- Ross, Malcolm & Andrew Pawley (1993). "Austronesian historical linguistics and culture history". Annual Review of Anthropology. 22: 425–459. doi:10.1146/annurev.an.22.100193.002233. OCLC 1783647.
- Ross, John (2002). "Final words: research themes in the history and typology of western Austronesian languages". In Wouk, Fay; Ross, Malcolm. The history and typology of Western Austronesian voice systems. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 451–474.
- Sagart, Laurent (8–11 January 2002). Sino-Tibeto-Austronesian: An updated and improved argument (PDF). Ninth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics (ICAL9). Canberra, Australia.
- Sagart, Laurent (2004). "The higher phylogeny of Austronesian and the position of Tai–Kadai". Oceanic Linguistics. 43 (2): 411–440. doi:10.1353/ol.2005.0012.
- Sagart, Laurent (2005). "Sino-Tibeto-Austronesian: An updated and improved argument". In Blench, Roger; Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia. The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: Routledge Curzon. pp. 161–176.
- Sapir, Edward (1968). "Time perspective in aboriginal American culture: a study in method". In Mandelbaum, D.G. Selected writings of Edward Sapir in language, culture and personality. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 389–467.
- Taylor, G. (1888). "A ramble through southern Formosa". The China Review. 16: 137–161.
- Terrell, John Edward (December 2004). "Introduction: 'Austronesia' and the great Austronesian migration". World Archaeology. 36 (4): 586–590. doi:10.1080/0043824042000303764.
- Thurgood, Graham (1999). "From Ancient Cham to Modern Dialects. Two Thousand Years of Language Contact and Change. Oceanic Linguistics Special Publications No. 28". Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press.
- Trejaut JA; Kivisild T; Loo JH; Lee CL; He CL (2005). "Traces of archaic mitochondrial lineages persist in Austronesian-speaking Formosan populations" (PDF). PLoS Biol. 3 (8): e247. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030247. PMC 1166350. PMID 15984912.
- Wouk, Fay and Malcolm Ross, eds. (2002), The history and typology of western Austronesian voice systems. Pacific Linguistics. Canberra: Australian National University.
Further reading[edit]
- Bengtson, John D., The "Greater Austric" Hypothesis, Association for the Study of Language in Prehistory.
- Blust, R. A. (1983). Lexical reconstruction and semantic reconstruction: the case of the Austronesian "house" words. Hawaii: R. Blust.
- Blust, Robert (2013). The Austronesian Languages (revised ed.). Australian National University. hdl:1885/10191. ISBN 978-1-922185-07-5.
- Cohen, E. M. K. (1999). Fundaments of Austronesian roots and etymology. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. ISBN 0-85883-436-7
- Marion, P., Liste Swadesh élargie de onze langues austronésiennes, éd. Carré de sucre, 2009
- Pawley, A., & Ross, M. (1994). Austronesian terminologies: continuity and change. Canberra, Australia: Dept. of Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, The Australian National University. ISBN 0-85883-424-3
- Sagart, Laurent, Roger Blench, and Alicia Sanchez-Nazas (Eds.) (2004). The peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0-415-32242-1.
- Tryon, D. T., & Tsuchida, S. (1995). Comparative Austronesian dictionary: an introduction to Austronesian studies. Trends in linguistics, 10. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 3110127296
- Wittmann, Henri (1972). "Le caractère génétiquement composite des changements phonétiques du malgache." Proceedings of the International Congress of Phonetic Sciences 7.807-10. La Haye: Mouton.
- Wolff, John U., "Comparative Austronesian Dictionary. An Introduction to Austronesian Studies", Language, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 145–56, Mar 1997, ISSN 0097-8507
External links[edit]
- Blust's Austronesian Comparative Dictionary
- Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database – ABVD (contains over 650 Austronesian Languages)
- Swadesh lists of Austronesian basic vocabulary words (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
- Summer Institute of Linguistics site showing languages (Austronesian and Papuan) of Papua New Guinea.
- Austronesian Language Resources (defunct? moved?) (Archived November 22, 2004, at the Wayback Machine)
- Spreadsheet of 1600+ Austronesian and Papuan number names and systems – ongoing study to determine their relationships and distribution[permanent dead link]
- Languages of the World: The Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian) Language Family
- Introduction to Austronesian Languages and Culture (video) (Malayo-Polynesian) Language Family on YouTube
- 南島語族分布圖



.png/500px-Chronological_dispersal_of_Austronesian_people_across_the_Pacific_(per_Bellwood_in_Chambers%2C_2008).png)