Siuslaw language
| Siuslaw | |
|---|---|
| Lower Umpqua | |
| Šáayušła / Quuiič | |
| Region | Oregon |
| Ethnicity | Siuslaw people |
| Extinct | 1970s |
Coast Oregon Penutian ?
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | sis |
| Glottolog | sius1254[1] |
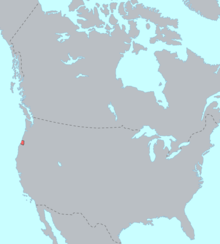 Pre-contact distribution of Siuslaw | |
Siuslaw /ˈsaɪjuːslɑː/ was the language of the Siuslaw people and Lower Umpqua (Kuitsh) people of Oregon. It is also known as Lower Umpqua; Upper Umpqua (or simply Umpqua) was an Athabaskan language. The Siuslaw language had two dialects: Siuslaw proper (Šaayušła) and Lower Umpqua (Quuiič).
Siuslaw is usually considered to belong to the Penutian phylum, and may form part of an Coast Oregon Penutian subgroup together with Alsea and the Coosan languages.[2]
Documentation[edit]
Published sources are by Leo J. Frachtenberg who collected data from a non-English-speaking native speaker of the Lower Umpqua dialect and her Alsean husband (who spoke it as a second language) during three months of fieldwork in 1911,[3][4][5] and by Dell Hymes who worked with four Siuslaw speakers in 1954.[6]
Further archived documentation consists of a 12-page vocabulary by James Owen Dorsey,[7] a wordlist of approximately 150 words taken by Melville Jacobs in 1935 in work with Lower Umpqua speaker Hank Johnson,[8] an audio recording of Siuslaw speaker Spencer Scott from 1941, hundreds of pages of notes from John Peabody Harrington in 1942 based on interviews with several native speakers,[9] and audio recordings of vocabulary by Morris Swadesh in 1953.
References[edit]
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Siuslaw". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ^ Grant, A. (1997). Coast Oregon Penutian: Problems and Possibilities. International Journal of American Linguistics, 63(1), 144-156.
- ^ Frachtenberg, Leo. (1914). Lower Umpqua texts and notes on the Kusan dialect. In Columbia University contributions to Anthropology (Vol. 4, pp. 151–150).
- ^ Frachtenberg, Leo Joachim; Franz Boas; Smithsonian Institution. Bureau of American Ethnology (1917). Siuslawan (Lower Umpqua): an illustrative sketch. Govt. Printing Office. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ^ Frachtenberg, Leo. (1922). Siuslawan (Lower Umpqua). In Handbook of American Indian languages (Vol. 2, pp. 431–629).
- ^ Hymes, Dell. (1966). Some points of Siuslaw phonology. International Journal of American Linguistics, 32, 328-342.
- ^ Dorsey, James Owen. (1884). [Siuslaw vocabulary, with sketch map showing villages, and incomplete key giving village names October 27, 1884]. Smithsonian Institution National Anthropological Archives.[1]
- ^ Melville Jacobs papers, 1918-1978, University of Washington Special Collections, Seattle WA.
- ^ Harrington, John P. 1942. "Alsea, SIuslaw, Coos, Southwest Oregon Athapaskan: Vocabularies, Linguistic Notes, Ethnographic and Historical Notes." John Peabody Harrington Papers, Alaska/Northwest Coast. National Anthropological Archives, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC.
External links[edit]
| This indigenous languages of the Americas–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- Coast Oregon Penutian languages
- Language isolates of North America
- Indigenous languages of the Pacific Northwest Coast
- Penutian languages
- Indigenous languages of Oregon
- Extinct languages of North America
- Languages extinct in the 1970s
- 1970s disestablishments in Oregon
- Indigenous languages of the Americas stubs